Explanatory deep learning to predict elevated pulmonary artery pressure in children with ventricular septal defects using standard chest x-rays: a novel approach
- PMID: 38283829
- PMCID: PMC10811002
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1330685
Explanatory deep learning to predict elevated pulmonary artery pressure in children with ventricular septal defects using standard chest x-rays: a novel approach
Abstract
Objective: Early risk assessment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) is crucial to ensure timely treatment. We hypothesize that applying artificial intelligence (AI) to chest x-rays (CXRs) could identify the future risk of PAH in patients with ventricular septal defect (VSD).
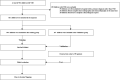
Methods: A total of 831 VSD patients (161 PAH-VSD, 670 nonPAH-VSD) was retrospectively included. A residual neural networks (ResNet) was trained for classify VSD patients with different outcomes based on chest radiographs. The endpoint of this study was the occurrence of PAH in VSD children before or after surgery.
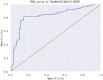
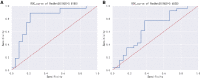
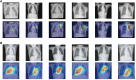
Results: In the validation set, the AI algorithm achieved an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.82. In an independent test set, the AI algorithm significantly outperformed human observers in terms of AUC (0.81 vs. 0.65). Class Activation Mapping (CAM) images demonstrated the model's attention focused on the pulmonary artery segment.
Conclusion: The preliminary findings of this study suggest that the application of artificial intelligence to chest x-rays in VSD patients can effectively identify the risk of PAH.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; chest x-ray; deep learning—artificial intelligence; pulmonary arterial hypertension; ventricular septal defect.
© 2024 Li, Luo, Ji, Wang and Pan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential diagnosis of congenital ventricular septal defect and atrial septal defect in children using deep learning-based analysis of chest radiographs.BMC Pediatr. 2024 Oct 15;24(1):661. doi: 10.1186/s12887-024-05141-y. BMC Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39407181 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence-assisted diagnosis of congenital heart disease and associated pulmonary arterial hypertension from chest radiographs: A multi-reader multi-case study.Eur J Radiol. 2024 Feb;171:111277. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2023.111277. Epub 2023 Dec 27. Eur J Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38160541
-
Deep learning to predict elevated pulmonary artery pressure in patients with suspected pulmonary hypertension using standard chest X ray.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 17;10(1):19311. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-76359-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33203947 Free PMC article.
-
Computational simulation-derived hemodynamic and biomechanical properties of the pulmonary arterial tree early in the course of ventricular septal defects.Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2021 Dec;20(6):2471-2489. doi: 10.1007/s10237-021-01519-4. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2021. PMID: 34585299 Free PMC article.
-
[Intermediate results of the integrated approach to pulmonary atresia with ventricular septal defect and major aortopulmonary collateral arteries].Ital Heart J Suppl. 2004 Feb;5(2):128-36. Ital Heart J Suppl. 2004. PMID: 15080532 Review. Italian.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

