Molecular Regulation and Oncogenic Functions of TSPAN8
- PMID: 38275818
- PMCID: PMC10814125
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13020193
Molecular Regulation and Oncogenic Functions of TSPAN8
Abstract
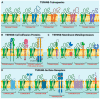
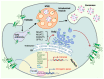
Tetraspanins, a superfamily of small integral membrane proteins, are characterized by four transmembrane domains and conserved protein motifs that are configured into a unique molecular topology and structure in the plasma membrane. They act as key organizers of the plasma membrane, orchestrating the formation of specialized microdomains called "tetraspanin-enriched microdomains (TEMs)" or "tetraspanin nanodomains" that are essential for mediating diverse biological processes. TSPAN8 is one of the earliest identified tetraspanin members. It is known to interact with a wide range of molecular partners in different cellular contexts and regulate diverse molecular and cellular events at the plasma membrane, including cell adhesion, migration, invasion, signal transduction, and exosome biogenesis. The functions of cell-surface TSPAN8 are governed by ER targeting, modifications at the Golgi apparatus and dynamic trafficking. Intriguingly, limited evidence shows that TSPAN8 can translocate to the nucleus to act as a transcriptional regulator. The transcription of TSPAN8 is tightly regulated and restricted to defined cell lineages, where it can serve as a molecular marker of stem/progenitor cells in certain normal tissues as well as tumors. Importantly, the oncogenic roles of TSPAN8 in tumor development and cancer metastasis have gained prominence in recent decades. Here, we comprehensively review the current knowledge on the molecular characteristics and regulatory mechanisms defining TSPAN8 functions, and discuss the potential and significance of TSPAN8 as a biomarker and therapeutic target across various epithelial cancers.
Keywords: TSPAN8; cancer metastasis; cancer stem cell; cell invasion; cell signaling; exosome; plasma membrane; stem cell; tetraspanin; tetraspanin-enriched microdomain; tumor-associated antigen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
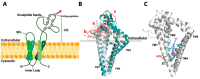

Similar articles
-
Sequential genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screens identify genes regulating cell-surface expression of tetraspanins.Cell Rep. 2023 Feb 28;42(2):112065. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112065. Epub 2023 Jan 31. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 36724073
-
TSPAN8 as a Novel Emerging Therapeutic Target in Cancer for Monoclonal Antibody Therapy.Biomolecules. 2020 Mar 3;10(3):388. doi: 10.3390/biom10030388. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32138170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Joint features and complementarities of Tspan8 and CD151 revealed in knockdown and knockout models.Biochem Soc Trans. 2017 Apr 15;45(2):437-447. doi: 10.1042/BST20160298. Biochem Soc Trans. 2017. PMID: 28408484 Review.
-
Tetraspanin 8 is a novel regulator of ILK-driven β1 integrin adhesion and signaling in invasive melanoma cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Mar 7;8(10):17140-17155. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15084. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28188308 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative characterization of tetraspanin 8 homointeractions in the plasma membrane.Biochem J. 2021 Oct 15;478(19):3643-3654. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20210459. Biochem J. 2021. PMID: 34524408 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

