Hypoxia represses FOXF1 in lung endothelial cells through HIF-1α
- PMID: 38274049
- PMCID: PMC10809398
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1309155
Hypoxia represses FOXF1 in lung endothelial cells through HIF-1α
Abstract
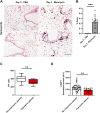
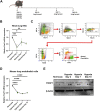
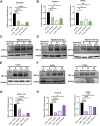
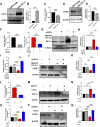
Introduction: Forkhead Box F1 (FOXF1) transcription factor plays a critical role in lung angiogenesis during embryonic development and lung repair after injury. FOXF1 expression is decreased in endothelial cells after lung injury; however, molecular mechanisms responsible for the FOXF1 transcript changes in injured lung endothelium remain unknown. Methods: We used immunostaining of injured mouse lung tissues, FACS-sorted lung endothelial cells from hypoxia-treated mice, and data from patients diagnosed with hypoxemic respiratory failure to demonstrate that hypoxia is associated with decreased FOXF1 expression. Endothelial cell cultures were used to induce hypoxia in vitro and identify the upstream molecular mechanism through which hypoxia inhibits FOXF1 gene expression. Results: Bleomycin-induced lung injury induced hypoxia in the mouse lung tissue which was associated with decreased Foxf1 expression. Human FOXF1 mRNA was decreased in the lungs of patients diagnosed with hypoxemic respiratory failure. Mice exposed to hypoxia exhibited reduced Foxf1 expression in the lung tissue and FACS-sorted lung endothelial cells. In vitro, hypoxia (1% of O2) or treatment with cobalt (II) chloride increased HIF-1α protein levels but inhibited FOXF1 expression in three endothelial cell lines. Overexpression of HIF-1α in cultured endothelial cells was sufficient to inhibit Foxf1 expression. siRNA-mediated depletion of HIF-1α prevented the downregulation of Foxf1 gene expression after hypoxia or cobalt (II) chloride treatment. Conclusion: Hypoxia inhibits FOXF1 expression in endothelial cells in a HIF-1α dependent manner. Our data suggest that endothelial cell-specific inhibition of HIF-1α via gene therapy can be considered to restore FOXF1 and improve lung repair in patients with severe lung injury.
Keywords: FOXF1; HIF-1α; endothelial cells; hypoxia; lung.
Copyright © 2024 Acharya, Bian, Gomez-Arroyo, Wagner, Kalinichenko and Kalin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Wild-type levels of the mouse Forkhead Box f1 gene are essential for lung repair.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2002 Jun;282(6):L1253-65. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00463.2001. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12003781
-
Endothelial Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Is Required for Vascular Repair and Resolution of Inflammatory Lung Injury through Forkhead Box Protein M1.Am J Pathol. 2019 Aug;189(8):1664-1679. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2019.04.014. Epub 2019 May 20. Am J Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31121134 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia Upregulates Estrogen Receptor β in Pulmonary Artery Endothelial Cells in a HIF-1α-Dependent Manner.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2018 Jul;59(1):114-126. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2017-0167OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29394091 Free PMC article.
-
A novel role of hypoxia-inducible factor in cobalt chloride- and hypoxia-mediated expression of IL-8 chemokine in human endothelial cells.J Immunol. 2006 Nov 15;177(10):7211-24. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.10.7211. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17082639
-
Postnatal Alveologenesis Depends on FOXF1 Signaling in c-KIT+ Endothelial Progenitor Cells.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019 Nov 1;200(9):1164-1176. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201812-2312OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019. PMID: 31233341 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aquino-Gálvez A., González-Ávila G., Jiménez-Sánchez L. L., Maldonado-Martínez H. A., Cisneros J., Toscano-Marquez F., et al. (2019). Dysregulated expression of hypoxia inducible factors augments myofibroblasts differentiation in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 20, 130. 10.1186/s12931-019-1100-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

