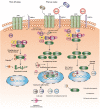
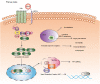
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in the tumor progression of adrenocortical carcinoma
- PMID: 38269250
- PMCID: PMC10806569
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1260701
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in the tumor progression of adrenocortical carcinoma
Abstract
Adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC) is an uncommon, aggressive endocrine malignancy with a high rate of recurrence, a poor prognosis, and a propensity for metastasis. Currently, only mitotane has received certification from both the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency for the therapy of advanced ACC. However, treatment in the advanced periods of the disorders is ineffective and has serious adverse consequences. Completely surgical excision is the only cure but has failed to effectively improve the survival of advanced patients. The aberrantly activated Wnt/β-catenin pathway is one of the catalysts for adrenocortical carcinogenesis. Research has concentrated on identifying methods that can prevent the stimulation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and are safe and advantageous for patients in view of the absence of effective treatments and the frequent alteration of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in ACC. Comprehending the complex connection between the development of ACC and Wnt/β-catenin signaling is essential for accurate pharmacological targets. In this review, we summarize the potential targets between adrenocortical carcinoma and the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. We analyze the relevant targets of drugs or inhibitors that act on the Wnt pathway. Finally, we provide new insights into how drugs or inhibitors may improve the treatment of ACC.
Keywords: Wnt/beta-catenin; adrenocortical carcinoma; cross talk; therapeutic targets; tumor progression.
Copyright © 2024 Tai and Shang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effects of mitotane and 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in human adrenocortical carcinoma cells.J Endocrinol Invest. 2020 Mar;43(3):357-367. doi: 10.1007/s40618-019-01127-1. Epub 2019 Oct 5. J Endocrinol Invest. 2020. PMID: 31587178
-
Rottlerin as a novel chemotherapy agent for adrenocortical carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 4;8(14):22825-22834. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15221. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28423559 Free PMC article.
-
BCL9 Upregulation in Adrenocortical Carcinoma: A Novel Wnt/β-Catenin Activating Event Driving Adrenocortical Malignancy.J Am Coll Surg. 2018 Jun;226(6):988-995. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2018.01.051. Epub 2018 Feb 8. J Am Coll Surg. 2018. PMID: 29428231
-
Update in adrenocortical carcinoma.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Dec;98(12):4551-64. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-3020. Epub 2013 Sep 30. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 24081734 Review.
-
New targeted therapies for adrenocortical carcinomas.Minerva Endocrinol. 2019 Mar;44(1):70-81. doi: 10.23736/S0391-1977.18.02860-2. Epub 2018 May 28. Minerva Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 29808641 Review.
Cited by
-
N-glycosylation of Wnt3 regulates the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by affecting Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Jun 15;16(6):2769-2780. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2769. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38994173 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Different Variants of Leptin Receptor in Human Adrenal Tumor Types.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 9;25(16):8682. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168682. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201370 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources