Impact of vitamin D supplementation as COVID-19 vaccine adjuvant on sperm parameters and sex hormones in men with idiopathic infertility: Two separate pre-post studies
- PMID: 38263587
- PMCID: PMC11140254
- DOI: 10.5653/cerm.2023.06464
Impact of vitamin D supplementation as COVID-19 vaccine adjuvant on sperm parameters and sex hormones in men with idiopathic infertility: Two separate pre-post studies
Abstract
Objective: Vitamin D deficiency is a major problem for human health worldwide. The mechanisms of vitamin D in the male reproductive system are unknown. After coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccines were developed, doubts were raised about their possible effects on male fertility. Based on vitamin D's function in the immune system, its potential role as an adjuvant for COVID-19 vaccines is intriguing. The aims of this study were to assess the effects of vitamin D first on sperm parameters and sex hormones, and then as an immune adjuvant on sperm parameters and sex hormones after study participants had received their second doses of COVID-19 vaccines.
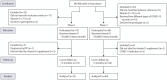
Methods: Phase 1 (before the COVID-19 pandemic) included 72 men with idiopathic infertility, and phase 2 had 64 participants who received two doses of COVID-19 vaccines. Both groups were instructed to take 50,000 IU of vitamin D twice monthly for 3 months. Sperm parameters and sex hormones were assessed pre- and post-supplementation.
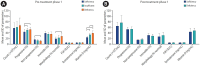
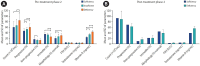
Results: Regular vitamin D intake for 3 months significantly increased the participants' vitamin D levels (p=0.0001). Both phases showed a positive correlation between vitamin D intake and sperm parameters. Vaccination had no negative effects on sperm parameters and sex hormones. Vitamin D was associated with follicle-stimulating hormone (p=0.02) and testosterone (p=0.0001) in phase 2 after treatment.
Conclusion: Our results support vitamin D supplementation as an immune adjunct to COVID-19 vaccination for improving sperm parameters and hormone levels. COVID-19 vaccination is not harmful for male fertility potential, and vitamin D is an effective factor for male fertility.
Keywords: COVID-19; Infertility; Sperm; Vaccines; Vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of the relationship between vitamin D with semen analysis parameters and reproductive hormones levels before and after kidney transplantation: An Iranian randomized and double-blinded study.Urologia. 2023 May;90(2):272-277. doi: 10.1177/03915603231162394. Epub 2023 Apr 3. Urologia. 2023. PMID: 37006175 Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation of the effect of vitamin D supplementation on spermatogram, seminal and serum levels of oxidative stress indices in asthenospermia infertile men: a study protocol for a triple-blind, randomized controlled trial.Nutr J. 2021 Jun 2;20(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s12937-021-00711-7. Nutr J. 2021. PMID: 34078367 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Serum Vitamin D Concentration with Spermiogram Parameters and Reproductive Hormones Among Infertile Iranian Males: a Cross-sectional Study.Reprod Sci. 2022 Jan;29(1):270-276. doi: 10.1007/s43032-021-00771-4. Epub 2021 Nov 11. Reprod Sci. 2022. PMID: 34766260
-
The Association between Vitamin D and the Components of Male Fertility: A Systematic Review.Biomedicines. 2022 Dec 29;11(1):90. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11010090. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36672602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combining vitamin A and vaccines: convenience or conflict?Dan Med J. 2012 Jan;59(1):B4378. Dan Med J. 2012. PMID: 22239846 Review.
References
-
- La Vignera S, Condorelli RA, Duca Y, Mongioi LM, Cannarella R, Giacone F, et al. FSH therapy for idiopathic male infertility: four schemes are better than one. Aging Male. 2020;23:750–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

