Hypoxia inducible factors inhibit respiratory syncytial virus infection by modulation of nucleolin expression
- PMID: 38261926
- PMCID: PMC10797196
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108763
Hypoxia inducible factors inhibit respiratory syncytial virus infection by modulation of nucleolin expression
Abstract
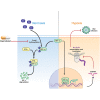
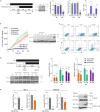
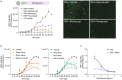
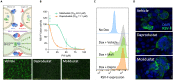
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a global healthcare problem, causing respiratory illness in young children and elderly individuals. Our knowledge of the host pathways that define susceptibility to infection and disease severity are limited. Hypoxia inducible factors (HIFs) define metabolic responses to low oxygen and regulate inflammatory responses in the lower respiratory tract. We demonstrate a role for HIFs to suppress RSV entry and RNA replication. We show that hypoxia and HIF prolyl-hydroxylase inhibitors reduce the expression of the RSV entry receptor nucleolin and inhibit viral cell-cell fusion. We identify a HIF regulated microRNA, miR-494, that regulates nucleolin expression. In RSV-infected mice, treatment with the clinically approved HIF prolyl-hydroxylase inhibitor, Daprodustat, reduced the level of infectious virus and infiltrating monocytes and neutrophils in the lung. This study highlights a role for HIF-signalling to limit multiple aspects of RSV infection and associated inflammation and informs future therapeutic approaches for this respiratory pathogen.
Keywords: Molecular biology; Omics; Transcriptomics;.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any competing interests to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypoxia-inducible-factors differentially contribute to clinical disease and viral replication during RSV infection.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 16:2023.08.15.553422. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.15.553422. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 37645750 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Depletion of TAX1BP1 Amplifies Innate Immune Responses during Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection.J Virol. 2021 Oct 27;95(22):e0091221. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00912-21. Epub 2021 Aug 25. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34431698 Free PMC article.
-
Global disease burden of and risk factors for acute lower respiratory infections caused by respiratory syncytial virus in preterm infants and young children in 2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregated and individual participant data.Lancet. 2024 Mar 30;403(10433):1241-1253. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00138-7. Epub 2024 Feb 14. Lancet. 2024. PMID: 38367641
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Efficacy of anti-RSV vaccination in preventing respiratory syncytial virus disease and severe illness in older adults: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials.Eur Geriatr Med. 2024 Oct;15(5):1215-1229. doi: 10.1007/s41999-024-01066-y. Epub 2024 Sep 26. Eur Geriatr Med. 2024. PMID: 39325332
Cited by
-
Oxygen-dependent histone lysine demethylase 4 restricts hepatitis B virus replication.J Biol Chem. 2024 Mar;300(3):105724. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.105724. Epub 2024 Feb 5. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38325742 Free PMC article.
-
Neurological Impact of Respiratory Viruses: Insights into Glial Cell Responses in the Central Nervous System.Microorganisms. 2024 Aug 20;12(8):1713. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12081713. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39203555 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shi T., McAllister D.A., O'Brien K.L., Simoes E.A.F., Madhi S.A., Gessner B.D., Polack F.P., Balsells E., Acacio S., Aguayo C., et al. Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children in 2015: a systematic review and modelling study. Lancet. 2017;390:946–958. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Grayson S.A., Griffiths P.S., Perez M.K., Piedimonte G. Detection of airborne respiratory syncytial virus in a pediatric acute care clinic. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2017;52:684–688. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 200838/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BBS/E/I/00007039/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/X020843/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBS/E/I/00007038/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/R022011/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

