Biomimetic Nano-Drug Delivery System: An Emerging Platform for Promoting Tumor Treatment
- PMID: 38260239
- PMCID: PMC10802790
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S442877
Biomimetic Nano-Drug Delivery System: An Emerging Platform for Promoting Tumor Treatment
Abstract
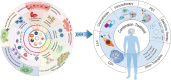
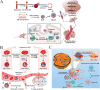
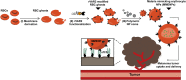
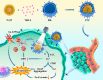
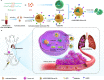
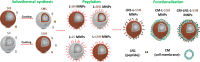
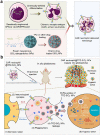
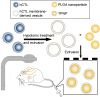
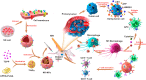
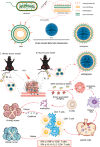
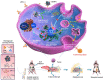
With the development of nanotechnology, nanoparticles (NPs) have shown broad prospects as drug delivery vehicles. However, they exhibit certain limitations, including low biocompatibility, poor physiological stability, rapid clearance from the body, and nonspecific targeting, which have hampered their clinical application. Therefore, the development of novel drug delivery systems with improved biocompatibility and high target specificity remains a major challenge. In recent years, biofilm mediated biomimetic nano-drug delivery system (BNDDS) has become a research hotspot focus in the field of life sciences. This new biomimetic platform uses bio-nanotechnology to encapsulate synthetic NPswithin biomimetic membrane, organically integrating the low immunogenicity, low toxicity, high tumor targeting, good biocompatibility of the biofilm with the adjustability and versatility of the nanocarrier, and shows promising applications in the field of precision tumor therapy. In this review, we systematically summarize the new progress in BNDDS used for optimizing drug delivery, providing a theoretical reference for optimizing drug delivery and designing safe and efficient treatment strategies to improve tumor treatment outcomes.
Keywords: cell membrane; nanoparticles; targeted therapy.
© 2024 Han et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Immunocyte membrane-derived biomimetic nano-drug delivery system: a pioneering platform for tumour immunotherapy.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024 Dec;45(12):2455-2473. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01355-z. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024. PMID: 39085407 Review.
-
Hybrid cell membrane-coated nanoparticles: A multifunctional biomimetic platform for cancer diagnosis and therapy.Acta Biomater. 2020 Aug;112:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.05.028. Epub 2020 May 26. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 32470527 Review.
-
Construction of Biomimetic-Responsive Nanocarriers and their Applications in Tumor Targeting.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022;22(12):2255-2273. doi: 10.2174/1871520622666220106105315. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 34994336
-
Application of Biomimetic Nanoparticles based on the Cell Membrane in Tumor Therapy.Curr Top Med Chem. 2023;23(10):907-920. doi: 10.2174/1568026623666230427114622. Curr Top Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37102484
-
The potential of biomimetic nanoparticles for tumor-targeted drug delivery.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2018 Aug;13(16):2099-2118. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2018-0017. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2018. PMID: 30226404 Review.
Cited by
-
Biomimetic ZIF-8 Nanoparticles: A Novel Approach for Biomimetic Drug Delivery Systems.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Jun 10;19:5523-5544. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S462480. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38882544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recognizing the biological barriers and pathophysiological characteristics of the gastrointestinal tract for the design and application of nanotherapeutics.Drug Deliv. 2024 Dec;31(1):2415580. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2024.2415580. Epub 2024 Oct 15. Drug Deliv. 2024. PMID: 39404464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advanced Nano-Drug Delivery Systems in the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke.Molecules. 2024 Apr 18;29(8):1848. doi: 10.3390/molecules29081848. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38675668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Composite Biofilm Biomimetic Nanodrug Delivery Systems for Cancer Treatment.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241250244. doi: 10.1177/15330338241250244. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 38693842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing Ovarian Cancer Therapeutics: The Role of Targeted Drug Delivery Systems.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Sep 10;19:9351-9370. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S478313. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39282574 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

