Functional electrospun nanofibers: fabrication, properties, and applications in wound-healing process
- PMID: 38259986
- PMCID: PMC10801448
- DOI: 10.1039/d3ra07075a
Functional electrospun nanofibers: fabrication, properties, and applications in wound-healing process
Abstract
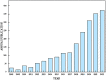
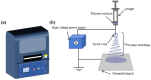
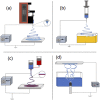
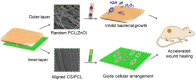
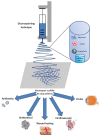
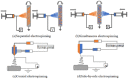
Electrostatic spinning as a technique for producing nanoscale fibers has recently attracted increasing attention due to its simplicity, versatility, and loadability. Nanofibers prepared by electrostatic spinning have been widely studied, especially in biomedical applications, because of their high specific surface area, high porosity, easy size control, and easy surface functionalization. Wound healing is a highly complex and dynamic process that is a crucial step in the body's healing process to recover from tissue injury or other forms of damage. Single-component nanofibers are more or less limited in terms of structural properties and do not fully satisfy various needs of the materials. This review aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the literature on the use of electrostatically spun nanofibers to promote wound healing, to overview the infinite possibilities for researchers to tap into their biomedical applications through functional composite modification of nanofibers for advanced and multifunctional materials, and to propose directions and perspectives for future research.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Electrospun nanofibers for wound healing.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017 Jul 1;76:1413-1423. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2017.03.034. Epub 2017 Mar 14. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017. PMID: 28482508 Review.
-
Advanced Metallized Nanofibers for Biomedical Applications.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Sep;10(27):e2302044. doi: 10.1002/advs.202302044. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37532670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Progress in Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile Nanofiber-Based Wound Dressing.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Aug 11;14(16):3266. doi: 10.3390/polym14163266. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36015523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrospun hybrid nanofibers: Fabrication, characterization, and biomedical applications.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Dec 1;10:986975. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.986975. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36561047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Naturally-derived electrospun wound dressings for target delivery of bio-active agents.Int J Pharm. 2019 Jul 20;566:307-328. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.05.053. Epub 2019 May 21. Int J Pharm. 2019. PMID: 31125714 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of Electrospun Drug-Loaded Nanofibers in Cancer Therapy.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Feb 12;16(4):504. doi: 10.3390/polym16040504. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38399882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancement of antibacterial activity in electrospun fibrous membranes based on quaternized chitosan with caffeic acid and berberine chloride for wound dressing applications.RSC Adv. 2024 Oct 30;14(47):34756-34768. doi: 10.1039/d4ra05114a. eCollection 2024 Oct 29. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39483382 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid films loaded with 5-fluorouracil and Reglan for synergistic treatment of colon cancer via asynchronous dual-drug delivery.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Jun 13;12:1398730. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1398730. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38938981 Free PMC article.
-
Polyethersulfone Polymer for Biomedical Applications and Biotechnology.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 11;25(8):4233. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084233. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38673817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent progress of electrospun nanofibers as burning dressings.RSC Adv. 2024 May 1;14(20):14374-14391. doi: 10.1039/d4ra01514b. eCollection 2024 Apr 25. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38694552 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xue C. Wilson L. D. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022;275:118751. - PubMed
-
- Al-Dhahebi A. M. Ling J. Krishnan S. G. Yousefzadeh M. Elumalai N. K. Saheed M. S. M. Ramakrishna S. Jose R. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2022;9:011319.
-
- Hu D. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 2022;58:1509–1517.
-
- Kamil A. I. Munir M. M. Powder Technol. 2023;430:118978.
-
- Drosou C. Krokida M. Biliaderis C. G. Food Hydrocolloids. 2022;133:107949.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

