Cortical and Striatal Astrocytes of Neonatal Rats Display Distinct Molecular and Pharmacological Characteristics of Dopamine Uptake
- PMID: 38255983
- PMCID: PMC10815805
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25020911
Cortical and Striatal Astrocytes of Neonatal Rats Display Distinct Molecular and Pharmacological Characteristics of Dopamine Uptake
Abstract
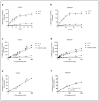
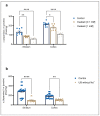
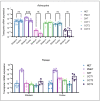
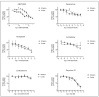
Astrocytes are crucial in the regulation of neurotransmitter homeostasis, and while their involvement in the dopamine (DA) tripartite synapse is acknowledged, it necessitates a more comprehensive investigation. In the present study, experiments were conducted on primary astrocyte cultures from the striatum and cortex of neonatal rats. The pharmacological intricacies of DA uptake, including dependence on time, temperature, and concentration, were investigated using radiolabelled [3H]-DA. The mRNA expression of transporters DAT, NET, PMAT, and OCTs was evaluated by qPCR. Notably, astrocytes from both brain regions exhibited prominent mRNA expression of NET and PMAT, with comparatively lower expression of DAT and OCTs. The inhibition of DA uptake by the DAT inhibitor, GBR12909, and NET inhibitors, desipramine and nortriptyline, impeded DA uptake in striatal astrocytes more than in cortical astrocytes. The mRNA expression of NET and PMAT was significantly upregulated in cortical astrocytes in response to the DA receptor agonist apomorphine, while only the mRNA expression of NET exhibited changes in striatal astrocytes. Haloperidol, a DA receptor antagonist, and L-DOPA, a DA precursor, did not induce significant alterations in transporter mRNA expression. These findings underscore the intricate and region-specific mechanisms governing DA uptake in astrocytes, emphasizing the need for continued exploration to unravel the nuanced dynamics of astrocytic involvement in the DA tripartite synapse.
Keywords: NET; PMAT; astrocyte; dopamine uptake; neonatal rat.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Kinetic Properties and Pharmacological Modulation of High- and Low-Affinity Dopamine Transport in Striatal Astrocytes of Adult Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 9;25(10):5135. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105135. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791173 Free PMC article.
-
Transporters involved in adult rat cortical astrocyte dopamine uptake: Kinetics, expression and pharmacological modulation.Eur J Neurosci. 2024 Mar;59(6):1296-1310. doi: 10.1111/ejn.16202. Epub 2023 Dec 6. Eur J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38054361
-
Dopamine transporter loss in 6-OHDA Parkinson's model is unmet by parallel reduction in dopamine uptake.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52322. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052322. Epub 2012 Dec 26. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23300642 Free PMC article.
-
Astroglial dopamine transport is mediated by norepinephrine transporter.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2002 Dec;366(6):620-3. doi: 10.1007/s00210-002-0640-0. Epub 2002 Sep 25. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12444505
-
Pharmacological treatment with L-DOPA may reduce striatal dopamine transporter binding in in vivo imaging studies.Nuklearmedizin. 2016;55(1):21-8. doi: 10.3413/Nukmed-0764-15-08. Epub 2015 Dec 7. Nuklearmedizin. 2016. PMID: 26642370 Review.
Cited by
-
Kinetic Properties and Pharmacological Modulation of High- and Low-Affinity Dopamine Transport in Striatal Astrocytes of Adult Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 9;25(10):5135. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105135. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791173 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

