Insights into the Neuroprotective Potential of Epicatechin: Effects against Aβ-Induced Toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 38247503
- PMCID: PMC10812808
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13010079
Insights into the Neuroprotective Potential of Epicatechin: Effects against Aβ-Induced Toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
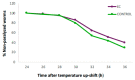
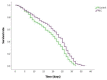
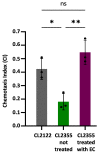
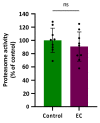
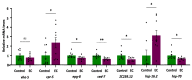
Medical therapies to avoid the progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD) are limited to date. Certain diets have been associated with a lower incidence of neurodegenerative diseases. In particular, the regular intake of foods rich in polyphenols, such as epicatechin (EC), could help prevent or mitigate AD progression. This work aims to explore the neuroprotective effects of EC using different transgenic strains of Caenorhabditis elegans, which express human Aβ1-42 peptides and contribute to elucidating the mechanisms involved in the effects of EC in AD. The performed assays indicate that this flavan-3-ol was able to reduce the signs of β-amyloid accumulation in C. elegans, improving motility and chemotaxis and increasing survival in transgenic strain peptide producers compared to nematodes not treated with EC. The neuroprotective effects exhibited by EC in C. elegans could be explained by the modulation of inflammation and stress-associated genes, as well as autophagy, microgliosis, and heat shock signaling pathways, involving the regulation of cpr-5, epg-8, ced-7, ZC239.12, and hsp-16 genes. Overall, the results obtained in this study support the protective effects of epicatechin against Aβ-induced toxicity.
Keywords: chemotaxis; flavonoids; gene expression; neuroprotection; paralysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
N-butanol extract of Hedyotis diffusa protects transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans from Aβ-induced toxicity.Phytother Res. 2021 Feb;35(2):1048-1061. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6871. Epub 2020 Sep 13. Phytother Res. 2021. PMID: 32924204
-
Inhibition of Abeta Proteotoxicity by Paeoniflorin in Caenorhabditis elegans Through Regulation of Oxidative and Heat Shock Stress Responses.Rejuvenation Res. 2018 Aug;21(4):304-312. doi: 10.1089/rej.2017.1966. Epub 2017 Dec 14. Rejuvenation Res. 2018. PMID: 29048250
-
Exploring the therapeutic potential of Nelumbo nucifera leaf extract against amyloid-beta-induced toxicity in the Caenorhabditis elegans model of Alzheimer's disease.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 24;15:1408031. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1408031. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38983916 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy Regulation Influences β-Amyloid Toxicity in Transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 May 12;14:885145. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.885145. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35645788 Free PMC article.
-
Caenorhabditis elegans Model for Initial Screening and Mechanistic Evaluation of Potential New Drugs for Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease.In: Buccafusco JJ, editor. Methods of Behavior Analysis in Neuroscience. 2nd edition. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2009. Chapter 16. In: Buccafusco JJ, editor. Methods of Behavior Analysis in Neuroscience. 2nd edition. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2009. Chapter 16. PMID: 21204333 Free Books & Documents. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

