Mechanisms of RNF168 nucleosome recognition and ubiquitylation
- PMID: 38242129
- PMCID: PMC10939898
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.12.036
Mechanisms of RNF168 nucleosome recognition and ubiquitylation
Abstract
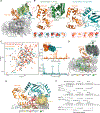
RNF168 plays a central role in the DNA damage response (DDR) by ubiquitylating histone H2A at K13 and K15. These modifications direct BRCA1-BARD1 and 53BP1 foci formation in chromatin, essential for cell-cycle-dependent DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair pathway selection. The mechanism by which RNF168 catalyzes the targeted accumulation of H2A ubiquitin conjugates to form repair foci around DSBs remains unclear. Here, using cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, and functional assays, we provide a molecular description of the reaction cycle and dynamics of RNF168 as it modifies the nucleosome and recognizes its ubiquitylation products. We demonstrate an interaction of a canonical ubiquitin-binding domain within full-length RNF168, which not only engages ubiquitin but also the nucleosome surface, clarifying how such site-specific ubiquitin recognition propels a signal amplification loop. Beyond offering mechanistic insights into a key DDR protein, our study aids in understanding site specificity in both generating and interpreting chromatin ubiquitylation.
Keywords: 53BP1; BRCA1-BARD1; DNA damage response; NMR spectroscopy; RNF168; UbcH5c; X-ray crystallography; chromatin; cryo-EM; nucleosome; ubiquitin ligase.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
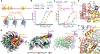

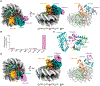
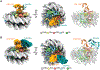
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of Ubiquitin-Nucleosome Recognition and Regulation of 53BP1 Chromatin Recruitment by RNF168/169 and RAD18.Mol Cell. 2017 May 18;66(4):473-487.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.04.009. Epub 2017 May 11. Mol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28506460 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of BRCA1-BARD1 nucleosome recognition and ubiquitylation.Nature. 2021 Aug;596(7872):438-443. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03716-8. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Nature. 2021. PMID: 34321665 Free PMC article.
-
BARD1 reads H2A lysine 15 ubiquitination to direct homologous recombination.Nature. 2021 Aug;596(7872):433-437. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03776-w. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Nature. 2021. PMID: 34321663
-
New answers to the old RIDDLE: RNF168 and the DNA damage response pathway.FEBS J. 2022 May;289(9):2467-2480. doi: 10.1111/febs.15857. Epub 2021 Apr 16. FEBS J. 2022. PMID: 33797206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk between histone modifications during the DNA damage response.Trends Cell Biol. 2009 May;19(5):207-17. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2009.03.001. Epub 2009 Apr 1. Trends Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19342239 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism of nucleosomal H2A K13/15 monoubiquitination and adjacent dual monoubiquitination by RNF168.Nat Chem Biol. 2024 Oct 11. doi: 10.1038/s41589-024-01750-x. Online ahead of print. Nat Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 39394267
-
Chemical Synthesis of Human Proteoforms and Application in Biomedicine.ACS Cent Sci. 2024 Jul 22;10(8):1442-1459. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.4c00642. eCollection 2024 Aug 28. ACS Cent Sci. 2024. PMID: 39220697 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Doil C, Mailand N, Bekker-Jensen S, Menard P, Larsen DH, Pepperkok R, Ellenberg J, Panier S, Durocher D, Bartek J, et al. (2009). RNF168 binds and amplifies ubiquitin conjugates on damaged chromosomes to allow accumulation of repair proteins. Cell 136, 435–446. 10.1016/j.cell.2008.12.041 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

