Spinal gout with intervertebral foramen infiltration: A rare case perfectly mimicking degenerative lumbar disc disease
- PMID: 38234610
- PMCID: PMC10792407
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2023.12354
Spinal gout with intervertebral foramen infiltration: A rare case perfectly mimicking degenerative lumbar disc disease
Abstract
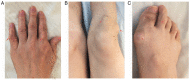
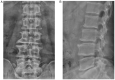
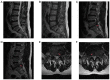
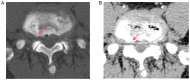
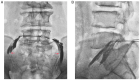
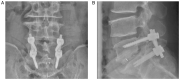
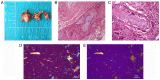
Spinal gout is a relatively rare disease characterized by significant clinical symptoms. In the current study, the first case of spinal gout with tophus in the intervertebral foramen, which perfectly mimicked degenerative lumbar disc disorders, was presented. The patient was a 57-year-old man with a medical history of gout who had suffered from progressive neurological deterioration for the last 12 months. Imaging examination revealed bilateral stenosis in the L5/S1 intervertebral foramen, mimicking degenerative lumbar disc disease. Nerve root radiculography and blocking were performed and the neurological symptoms were completely relieved. Open surgery was further performed and unexpectedly, the intra-operative findings were amorphous chalky white lesions. Histopathology confirmed the diagnosis of spinal gout. After surgery, the patient was prescribed a medication and achieved complete remission of clinical symptoms. No deterioration was found at the 1-year follow-up. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of spinal gout tophus in intervertebral foramen in the literature. It was concluded that, although intraspinal tophaceous gout is relatively rare, orthopedic surgeons should take it into consideration as a differential diagnosis, particularly if the patient has a medical history of gout. Early diagnosis and timely medical management may possibly be able to avoid neurological compromise and the need for surgery.
Keywords: intervertebral foramen; spinal gout; tophaceous gout.
Copyright: © Hu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tophaceous gout of the lumbar spine mimicking a spinal meningioma.Eur Spine J. 2018 Apr;27(4):815-819. doi: 10.1007/s00586-016-4831-7. Epub 2016 Nov 5. Eur Spine J. 2018. PMID: 27817138
-
Percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic decompression for the treatment of intraspinal tophaceous gout: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 May 22;99(21):e20125. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000020125. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32481280 Free PMC article.
-
Lumbar spinal stenosis attributable to tophaceous gout: case report and review of the literature.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2017 Sep 28;13:1287-1293. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S145906. eCollection 2017. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2017. PMID: 29033576 Free PMC article.
-
Tophaceous gout of the spine mimicking epidural infection: case report and review of the literature.Neurosurgery. 2001 May;48(5):1170-2; discussion 1172-3. doi: 10.1097/00006123-200105000-00046. Neurosurgery. 2001. PMID: 11334288 Review.
-
Tophaceous gout causing thoracic spinal cord compression: Case report and review of the literature.Neurochirurgie. 2018 Jun;64(3):171-176. doi: 10.1016/j.neuchi.2017.11.002. Epub 2018 May 3. Neurochirurgie. 2018. PMID: 29731313 Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
