Lnc-PSMA8-1 activated by GEFT promotes rhabdomyosarcoma progression via upregulation of mTOR expression by sponging miR-144-3p
- PMID: 38225540
- PMCID: PMC10789031
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-023-11798-y
Lnc-PSMA8-1 activated by GEFT promotes rhabdomyosarcoma progression via upregulation of mTOR expression by sponging miR-144-3p
Abstract
Background: GEFT is a key regulator of tumorigenesis in rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS), and overexpression of GEFT is significantly correlated with distant metastasis, lymph node metastasis, and a poor prognosis, yet the underlying molecular mechanism is still poorly understood. This study aimed to investigate and validate the molecular mechanism of GEFT-activated lncRNAs in regulating mTOR expression to promote the progression of RMS.
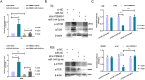
Methods: GEFT-regulated lncRNAs were identified through microarray analysis. The effects of GEFT-regulated lncRNAs on the proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, and migration of RMS cells were confirmed through cell functional experiments. The target miRNAs of GEFT-activated lncRNAs in the regulation of mTOR expression were predicted by bioinformatics analysis combined with quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) analysis. The expression of lnc-PSMA8-1, miR-144-3p, and mTOR was measured by qRT-PCR in RMS tissue samples and cell lines. The regulatory mechanisms of the lnc-PSMA8-1-miR-144-3p-mTOR signaling axis were verified by RNA-binding protein immunoprecipitation (RIP), a luciferase reporter assay, qRT-PCR analysis, Western blot analysis, and cell functional experiments.
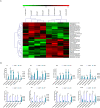
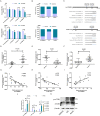
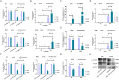
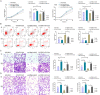
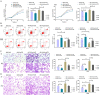
Results: The microarray-based analysis identified 31 differentially expressed lncRNAs (fold change > 2.0, P < 0.05). Silencing the 4 upregulated lncRNAs (lnc-CEACAM19-1, lnc-VWCE-2, lnc-GPX7-1, and lnc-PSMA8-1) and overexpressing the downregulated lnc-FAM59A-1 inhibited the proliferation, invasion, and migration and induced the apoptosis of RMS cells. Among the factors analyzed, the expression of lnc-PSMA8-1, miR-144-3p, and mTOR in RMS tissue samples and cells was consistent with the correlations among their expression indicated by the lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network based on the ceRNA hypothesis. lnc-PSMA8-1 promoted RMS progression by competitively binding to miR-144-3p to regulate mTOR expression.
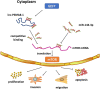
Conclusion: Our research demonstrated that lnc-PSMA8-1 was activated by GEFT and that the former positively regulated mTOR expression by sponging miR-144-3p to promote the progression of RMS. Therefore, targeting this network may constitute a potential therapeutic approach for the management of RMS.
Keywords: GEFT; Rhabdomyosarcoma; ceRNA; lnc-PSMA8-1; mTOR; miR-144-3p.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Downregulation of lncRNA ZEB1-AS1 Represses Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion Through Mediating PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling by miR-342-3p/CUL4B Axis in Prostate Cancer.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2020 Nov;35(9):661-672. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2019.3123. Epub 2020 Apr 9. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2020. PMID: 32275162
-
MicroRNA-874 functions as a tumor suppressor in rhabdomyosarcoma by directly targeting GEFT.Am J Cancer Res. 2019 Apr 1;9(4):668-681. eCollection 2019. Am J Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31105995 Free PMC article.
-
m6A-Mediated Upregulation of lncRNA CHASERR Promotes the Progression of Glioma by Modulating the miR-6893-3p/TRIM14 Axis.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Aug;61(8):5418-5440. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03911-w. Epub 2024 Jan 9. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38193984
-
Identification and bioinformatics analysis of lncRNAs in serum of patients with ankylosing spondylitis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Apr 15;25(1):291. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07396-z. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 38622662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRNAs as Interconnectors between Obesity and Cancer.Noncoding RNA. 2024 Apr 15;10(2):24. doi: 10.3390/ncrna10020024. Noncoding RNA. 2024. PMID: 38668382 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LINC02466 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through the mTOR pathway.Discov Oncol. 2024 Nov 6;15(1):623. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-00999-x. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39503938 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bompas E, Campion L, Italiano A, Le Cesne A, Chevreau C, Isambert N, Toulmonde M, Mir O, Ray-Coquard I, Piperno-Neumann S, et al. Outcome of 449 adult patients with rhabdomyosarcoma: an observational ambispective nationwide study. Cancer Med. 2018;7(8):4023–35. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1374. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

