To kill a microRNA: emerging concepts in target-directed microRNA degradation
- PMID: 38224449
- PMCID: PMC10899785
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae003
To kill a microRNA: emerging concepts in target-directed microRNA degradation
Abstract
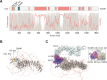
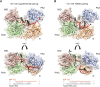
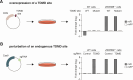
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) guide Argonaute (AGO) proteins to bind mRNA targets. Although most targets are destabilized by miRNA-AGO binding, some targets induce degradation of the miRNA instead. These special targets are also referred to as trigger RNAs. All triggers identified thus far have binding sites with greater complementarity to the miRNA than typical target sites. Target-directed miRNA degradation (TDMD) occurs when trigger RNAs bind the miRNA-AGO complex and recruit the ZSWIM8 E3 ubiquitin ligase, leading to AGO ubiquitination and proteolysis and subsequent miRNA destruction. More than 100 different miRNAs are regulated by ZSWIM8 in bilaterian animals, and hundreds of trigger RNAs have been predicted computationally. Disruption of individual trigger RNAs or ZSWIM8 has uncovered important developmental and physiologic roles for TDMD across a variety of model organisms and cell types. In this review, we highlight recent progress in understanding the mechanistic basis and functions of TDMD, describe common features of trigger RNAs, outline best practices for validating trigger RNAs, and discuss outstanding questions in the field.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


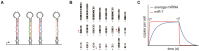
Similar articles
-
The ZSWIM8 ubiquitin ligase mediates target-directed microRNA degradation.Science. 2020 Dec 18;370(6523):eabc9359. doi: 10.1126/science.abc9359. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Science. 2020. PMID: 33184237 Free PMC article.
-
Widespread microRNA degradation elements in target mRNAs can assist the encoded proteins.Genes Dev. 2021 Dec 1;35(23-24):1595-1609. doi: 10.1101/gad.348874.121. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Genes Dev. 2021. PMID: 34819352 Free PMC article.
-
A ubiquitin ligase mediates target-directed microRNA decay independently of tailing and trimming.Science. 2020 Dec 18;370(6523):eabc9546. doi: 10.1126/science.abc9546. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Science. 2020. PMID: 33184234 Free PMC article.
-
Target-directed microRNA degradation: Mechanisms, significance, and functional implications.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2024 Mar-Apr;15(2):e1832. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1832. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2024. PMID: 38448799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA turnover: a tale of tailing, trimming, and targets.Trends Biochem Sci. 2023 Jan;48(1):26-39. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2022.06.005. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Trends Biochem Sci. 2023. PMID: 35811249 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide and cell-type-selective profiling of in vivo small noncoding RNA:target RNA interactions by chimeric RNA sequencing.Cell Rep Methods. 2024 Aug 19;4(8):100836. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2024.100836. Epub 2024 Aug 9. Cell Rep Methods. 2024. PMID: 39127045 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs, endometrial receptivity and molecular pathways.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2024 Nov 11;22(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s12958-024-01304-9. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 39529197 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Treiber T., Treiber N., Meister G. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis and its crosstalk with other cellular pathways. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019; 20:5–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

