Efficacy of Tounongsan decoction on pyogenic liver abscess: network pharmacology and clinical trial validation
- PMID: 38213249
- PMCID: PMC10774731
- DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20231110.006
Efficacy of Tounongsan decoction on pyogenic liver abscess: network pharmacology and clinical trial validation
Abstract
Objective: To elucidate the molecular mechanisms governing the effect of Tounongsan decoction (, TNS) on the pyogenic liver abscess.
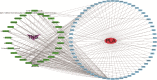
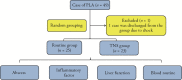
Methods: Based on oral bioavailability and drug-likeness, the main active components of TNS were screened using the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology platform. The GeneCard and UniProt databases were used to establish a database of pyogenic liver abscess targets. The interactive network map of drug-ingredients-target-disease was constructed using Cytoscape software (Version 3.7.2). A protein-protein interaction network was constructed using the STRING database, and the related protein interaction relationships were analyzed. biological process of gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analyses were performed for the core targets. Finally, a clinical trial was performed to verify the reliability of the network pharmacology.
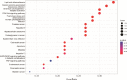
Results: Forty active components of TNS decoction were obtained, and 61 potential targets and 11 proteins were identified. Pathways involved in the treatment of pyogenic liver abscess include the phosphatidylinositide 3-kinases-protein kinase B (PI3K-AKT), advanced glycation end products-receptor for advanced glycation end products (AGE-RAGE), and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) signaling pathways. The results of network pharmacology analysis combined with clinical trials validated that TNS decoction could alleviate the inflammatory response of pyogenic liver abscesses by decreasing interleukin 6 (IL-6) levels.
Conclusions: TNS decoction has the characteristics of being multi-system, multi-component, and multi-target. Active ingredients in TNS, such as quercetin, kaempferol, fisetin, and β-sitosterol, have strong potential to be candidate drugs for treating pyogenic liver abscesses. The possible mechanism of TSN decoction includes regulating immune and inflammatory responses and reducing IL-6 production to control inflammatory development.
Keywords: Tounongsan decoction; clinical trial; liver abscess, pyogenic; network pharmacology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Using ultra-performance liquid chromatography with linear ion trap-electrostatic field orbitrap mass spectrometry, network pharmacology, and molecular docking to explore the constituent targets and action mechanisms of decoction of Angelica sinensis, Zingiberis Rhizoma Recens, and Mutton in the treatment of diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2024 May 3;76(5):462-478. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgad076. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37832514
-
The Network Pharmacology Study of Dahuang Fuzi Decoction for Treating Incomplete Intestinal Obstruction.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Apr 28;2022:2775434. doi: 10.1155/2022/2775434. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35528155 Free PMC article.
-
Observational study on the potential mechanism of Sanao decoction in the treatment of asthma based on network pharmacology and molecular docking.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Mar 22;103(12):e37592. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037592. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38518018 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Zisheng Shenqi decoction against gout arthritis using network pharmacology.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Feb;90:107358. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107358. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33243703 Review.
-
Exploring the molecular mechanism of Ling-Gui-Zhu-Gan decoction for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus based on network pharmacology and molecular docking: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Mar 24;102(12):e33210. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033210. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 36961137 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Qi L. Correlation between expression levels of peripheral blood T lymphocyte subsets and prognosis in patients with bacterial liver abscess and type 2 diabetes. Shanxi Yi Xue Za Zhi 2021; 50: 1510-2+6.
-
- Nikolakis G, Karagiannidis I, Vaiopoulos AG, Becker M, Zouboulis CC. Endocrinological mechanisms in the pathophysiology of hidradenitis suppurativa. Hautarzt 2020; 71: 762-71. - PubMed
-
- Tchana-Sato V, Hans G, Frippiat F, et al.. Surgical management of staphylococcus capitis prosthetic valve infective endocarditis: retrospective review of a 10-year single center experience and review of the literature. J Infect Public Health 2020; 13: 1705-9. - PubMed
-
- Antony S, Cooper L. Spontaneous chest abscess caused by salmonella enterica subsp. Arizonae in the desert southwest; a case report and review of the current literature. Infect Disord Drug Targets 2020; 20: 401-5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- YB201814/Jiangsu Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine: Clinical Study of TNS Combined with Puncture Catheter Drainage in the Treatment of PLA
- ZR2021016/Natural Fund of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine: Study on Promoting Glycolysis and Regulating Immune Microenvironment in Gastric Cancer MAIT Cells
- BE2022819/Natural Science Foudation of Jiangsu Province: the DextRan/Sore Spirit Complex Hydrogel was created in a Multicenter Study in the Treatment of Chronic Refractory Sores
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

