Levels of peripheral blood routine, biochemical and coagulation parameters in patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome and their relationship with prognosis: an observational cohort study
- PMID: 38212688
- PMCID: PMC10782698
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-023-08777-w
Levels of peripheral blood routine, biochemical and coagulation parameters in patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome and their relationship with prognosis: an observational cohort study
Abstract
Background: Hantaan virus (HTNV), Seoul virus (SEOV) and Puumala virus (PUUV) are major serotypes of the Hantavirus, which can cause hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS). The pathophysiology of HFRS in humans is complex and the determinants associated with mortality, especially the coagulation and fibrinolysis disorders, are still not been fully elucidated. Severe patients usually manifest multiple complications except for acute kidney injury (AKI). The aim of this study was to observe the levels of peripheral blood routine, biochemical and coagulation parameters during the early stage, so as to find independent risk factors closely related to the prognosis, which may provide theoretical basis for targeted treatment and evaluation.
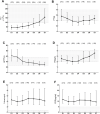
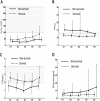
Methods: A total of 395 HFRS patients from December 2015 to December 2018 were retrospectively enrolled. According to prognosis, they were divided into a survival group (n = 368) and a death group (n = 27). The peripheral blood routine, biochemical and coagulation parameters were compared between the two groups on admission. The relationship between the parameters mentioned above and prognosis was analyzed, and the dynamic changes of the coagulation and fibrinolysis parameters during the first week after admission were further observed.
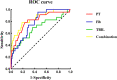
Results: In addition to AKI, liver injury was also common among the enrolled patients. Patients in the death group manifested higher levels of white blood cell counts (WBC) on admission. 27.30% (107/392) of the patients enrolled presented with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) on admission and DIC is more common in the death group; The death patients manifested longer prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), higher D-dimer and fibrinogen degradation product (FDP), and lower levels of platelets (PLT) and fibrinogen (Fib) compared with those of the survival patients. The proportion of D-dimer and FDP abnormalities are higher than PT, APTT and Fib. Prolonged PT, low level of Fib and elevated total bilirubin (TBIL) on admission were considered as independent risk factors for prognosis (death).
Conclusions: Detection of PT, Fib and TBIL on admission is necessary, which might be benefit to early predicting prognosis. It is also important to pay attention to the dynamic coagulation disorders and hyperfibrinolysis during the early stage in the severe HFRS patients.
Keywords: Coagulation parameters; Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome; Hyperfibrinolysis; Prognosis; Risk factors.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Study on the value of prothrombin time for predicting the severity and prognosis of septic patients].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022 Jul;34(7):682-688. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20210614-00876. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022. PMID: 36100403 Chinese.
-
[Establishment and validation of a risk prediction model for disseminated intravascular coagulation patients with electrical burns].Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2023 Aug 20;39(8):738-745. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501225-20230419-00132. Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37805784 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Study on expression of plasma sCD138 in patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome.BMC Infect Dis. 2018 Mar 1;18(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-3005-0. BMC Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29490629 Free PMC article.
-
Coagulopathy in Acute Puumala Hantavirus Infection.Viruses. 2021 Aug 6;13(8):1553. doi: 10.3390/v13081553. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34452419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disseminated intravascular coagulation with a fibrinolytic phenotype at an early phase of trauma predicts mortality.Thromb Res. 2009 Nov;124(5):608-13. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2009.06.034. Epub 2009 Aug 5. Thromb Res. 2009. PMID: 19660788 Review.
Cited by
-
Elevated Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time as a Predictor of 28-Day Mortality in Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis.Int J Gen Med. 2024 Apr 30;17:1739-1753. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S459583. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 38706747 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2021LC2222/General Clinical Research Project of Air Force Medical University
- 2022A011/Key Support Project in Hygiene and Health of Shaanxi Province
- 2021LCYJ025/Routine Clinical Research Program of the Second Affiliated Hospital of the Air Force Medical University
- 2023-ZDLSF-32/Key Industry Innovation Cluster Project: Social Development Field
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

