Palmitate Stimulates Expression of the von Willebrand Factor and Modulates Toll-like Receptors Level and Activity in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVECs)
- PMID: 38203423
- PMCID: PMC10779284
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25010254
Palmitate Stimulates Expression of the von Willebrand Factor and Modulates Toll-like Receptors Level and Activity in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVECs)
Abstract
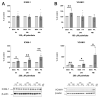
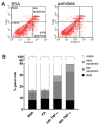
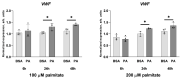
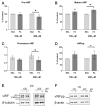
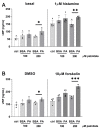
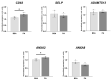
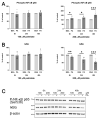
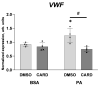
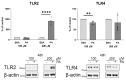
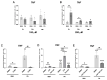
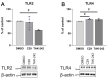
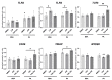
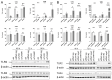
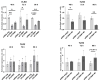
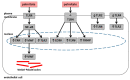
An increased concentration of palmitate in circulation is one of the most harmful factors in obesity. The von Willebrand factor (vWF), a protein involved in haemostasis, is produced and secreted by the vascular endothelium. An increased level of vWF in obese patients is associated with thrombosis and cardiovascular disease. The aim of this study was to investigate a palmitate effect on vWF in endothelial cells and understand the mechanisms of palmitate-activated signalling. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) incubated in the presence of palmitate, exhibited an increased VWF gene expression, vWF protein maturation, and stimulated vWF secretion. Cardamonin, a Nuclear Factor kappa B (NF-κB) inhibitor, abolished the palmitate effect on VWF expression. The inhibition of Toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 with C29 resulted in the TLR4 overactivation in palmitate-treated cells. Palmitate, in the presence of TLR4 inhibitor TAK-242, leads to a higher expression of TLR6, CD36, and TIRAP. The silencing of TLR4 resulted in an increase in TLR2 level and vice versa. The obtained results indicate a potential mechanism of obesity-induced thrombotic complication caused by fatty acid activation of NF-κB signalling and vWF upregulation and help to identify various compensatory mechanisms related to TLR4 signal transduction.
Keywords: NF-κB; TLR2; TLR4; endothelium; palmitate; von Willebrand factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Palmitate induces interleukin-8 expression in human aortic vascular smooth muscle cells via Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-κB pathway (TLR4/NF-κB-8).J Diabetes. 2014 Jan;6(1):33-41. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12073. Epub 2013 Aug 1. J Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 23826669
-
Induction of endothelial cell proliferation and von Willebrand factor expression and secretion by leukemic plasma of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia before and after inhibition of NF-κB.Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2016 Sep;27(6):711-6. doi: 10.1097/MBC.0000000000000502. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2016. PMID: 27472040
-
Low dose cadmium upregulates the expression of von Willebrand factor in endothelial cells.Toxicol Lett. 2018 Jun 15;290:46-54. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2018.03.020. Epub 2018 Mar 20. Toxicol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29571895
-
Heme triggers TLR4 signaling leading to endothelial cell activation and vaso-occlusion in murine sickle cell disease.Blood. 2014 Jan 16;123(3):377-90. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-04-495887. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Blood. 2014. PMID: 24277079 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of NF-kappaB by palmitate in endothelial cells: a key role for NADPH oxidase-derived superoxide in response to TLR4 activation.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009 Sep;29(9):1370-5. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.188813. Epub 2009 Jun 18. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009. PMID: 19542021 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fryk E., Olausson J., Mossberg K., Strindberg L., Schmelz M., Brogren H., Gan L.-M., Piazza S., Provenzani A., Becattini B., et al. Hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance in the obese may develop as part of a homeostatic response to elevated free fatty acids: A mechanistic case-control and a population-based cohort study. EBioMedicine. 2021;65:103264. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103264. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

