Deep Learning Model Based on You Only Look Once Algorithm for Detection and Visualization of Fracture Areas in Three-Dimensional Skeletal Images
- PMID: 38201320
- PMCID: PMC10802847
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14010011
Deep Learning Model Based on You Only Look Once Algorithm for Detection and Visualization of Fracture Areas in Three-Dimensional Skeletal Images
Abstract
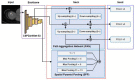
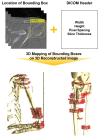
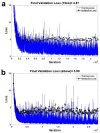
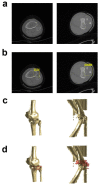
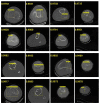
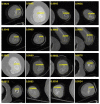
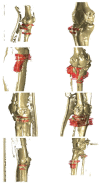
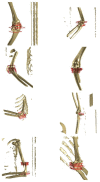
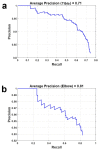
Utilizing "You only look once" (YOLO) v4 AI offers valuable support in fracture detection and diagnostic decision-making. The purpose of this study was to help doctors to detect and diagnose fractures more accurately and intuitively, with fewer errors. The data accepted into the backbone are diversified through CSPDarkNet-53. Feature maps are extracted using Spatial Pyramid Pooling and a Path Aggregation Network in the neck part. The head part aggregates and generates the final output. All bounding boxes by the YOLO v4 are mapped onto the 3D reconstructed bone images after being resized to match the same region as shown in the 2D CT images. The YOLO v4-based AI model was evaluated through precision-recall (PR) curves and the intersection over union (IoU). Our proposed system facilitated an intuitive display of the fractured area through a distinctive red mask overlaid on the 3D reconstructed bone images. The high average precision values (>0.60) were reported as 0.71 and 0.81 from the PR curves of the tibia and elbow, respectively. The IoU values were calculated as 0.6327 (tibia) and 0.6638 (elbow). When utilized by orthopedic surgeons in real clinical scenarios, this AI-powered 3D diagnosis support system could enable a quick and accurate trauma diagnosis.
Keywords: YOLO v4; deep learning; fracture detection; three dimensional (3D) reconstructed image; tibia and elbow.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors H.-Y.C., M.-S.K., J.-Y.Y., H.-J.K. and D.-K.Y. were employed by the company KAVILAB Co. Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Real-Time Pattern-Recognition of GPR Images with YOLO v3 Implemented by Tensorflow.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Nov 12;20(22):6476. doi: 10.3390/s20226476. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33198420 Free PMC article.
-
ACF Based Region Proposal Extraction for YOLOv3 Network Towards High-Performance Cyclist Detection in High Resolution Images.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Jun 13;19(12):2671. doi: 10.3390/s19122671. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31200511 Free PMC article.
-
ETL-YOLO v4: A face mask detection algorithm in era of COVID-19 pandemic.Optik (Stuttg). 2022 Jun;259:169051. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2022.169051. Epub 2022 Apr 7. Optik (Stuttg). 2022. PMID: 35411120 Free PMC article.
-
A hybrid tiny YOLO v4-SPP module based improved face mask detection vision system.J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput. 2023;14(6):6783-6796. doi: 10.1007/s12652-021-03541-x. Epub 2021 Oct 20. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput. 2023. PMID: 34691278 Free PMC article.
-
An Innovative Deep Learning Approach to Spinal Fracture Detection in CT Images.Ann Ital Chir. 2024;95(4):657-668. doi: 10.62713/aic.3498. Ann Ital Chir. 2024. PMID: 39186337
Cited by
-
Clinical validation of a deep learning-based approach for preoperative decision-making in implant size for total knee arthroplasty.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Oct 8;19(1):637. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05128-6. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 39380122 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Juan R., Diana M. A comprehensive review of YOLO: From YOLOv1 and beyond. arXiv. 20232304.00501
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

