Structural basis for transcription activation by the nitrate-responsive regulator NarL
- PMID: 38197271
- PMCID: PMC10853779
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkad1231
Structural basis for transcription activation by the nitrate-responsive regulator NarL
Abstract
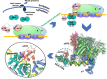
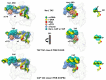
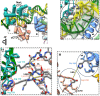
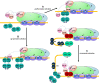
Transcription activation is a crucial step of regulation during transcription initiation and a classic check point in response to different stimuli and stress factors. The Escherichia coli NarL is a nitrate-responsive global transcription factor that controls the expression of nearly 100 genes. However, the molecular mechanism of NarL-mediated transcription activation is not well defined. Here we present a cryo-EM structure of NarL-dependent transcription activation complex (TAC) assembled on the yeaR promoter at 3.2 Å resolution. Our structure shows that the NarL dimer binds at the -43.5 site of the promoter DNA with its C-terminal domain (CTD) not only binding to the DNA but also making interactions with RNA polymerase subunit alpha CTD (αCTD). The key role of these NarL-mediated interactions in transcription activation was further confirmed by in vivo and in vitro transcription assays. Additionally, the NarL dimer binds DNA in a different plane from that observed in the structure of class II TACs. Unlike the canonical class II activation mechanism, NarL does not interact with σ4, while RNAP αCTD is bound to DNA on the opposite side of NarL. Our findings provide a structural basis for detailed mechanistic understanding of NarL-dependent transcription activation on yeaR promoter and reveal a potentially novel mechanism of transcription activation.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Definition of nitrite and nitrate response elements at the anaerobically inducible Escherichia coli nirB promoter: interactions between FNR and NarL.Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jan;7(1):151-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01106.x. Mol Microbiol. 1993. PMID: 8437517
-
The Escherichia coli NarL receiver domain regulates transcription through promoter specific functions.BMC Microbiol. 2015 Aug 26;15:174. doi: 10.1186/s12866-015-0502-9. BMC Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26307095 Free PMC article.
-
Nitrate and nitrite regulation of the Fnr-dependent aeg-46.5 promoter of Escherichia coli K-12 is mediated by competition between homologous response regulators (NarL and NarP) for a common DNA-binding site.J Mol Biol. 1995 Aug 4;251(1):15-29. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0412. J Mol Biol. 1995. PMID: 7643383
-
Nitrate regulation of anaerobic respiratory gene expression in Escherichia coli.Mol Microbiol. 1993 Aug;9(3):425-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01704.x. Mol Microbiol. 1993. PMID: 8412692 Review.
-
Transcription activation by catabolite activator protein (CAP).J Mol Biol. 1999 Oct 22;293(2):199-213. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3161. J Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10550204 Review.
Cited by
-
A conserved inhibitory interdomain interaction regulates DNA-binding activities of hybrid two-component systems in Bacteroides.mBio. 2024 Jul 17;15(7):e0122024. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01220-24. Epub 2024 Jun 6. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38842315 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Browning D.F., Butala M., Busby S.J.W.. Bacterial transcription factors: regulation by pick “N” mix. J. Mol. Biol. 2019; 431:4067–4077. - PubMed
-
- Browning D.F., Busby S.J.W.. Local and global regulation of transcription initiation in bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016; 14:638–650. - PubMed
-
- Libis V., Delépine B., Faulon J.L.. Sensing new chemicals with bacterial transcription factors. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2016; 33:105–112. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

