Exploratory Biomarker Analysis Using Plasma Angiogenesis-Related Factors and Cell-Free DNA in the TRUSTY Study: A Randomized, Phase II/III Study of Trifluridine/Tipiracil Plus Bevacizumab as Second-Line Treatment for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 38194163
- PMCID: PMC10830797
- DOI: 10.1007/s11523-023-01027-8
Exploratory Biomarker Analysis Using Plasma Angiogenesis-Related Factors and Cell-Free DNA in the TRUSTY Study: A Randomized, Phase II/III Study of Trifluridine/Tipiracil Plus Bevacizumab as Second-Line Treatment for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
Background: The TRUSTY study evaluated the efficacy of second-line trifluridine/tipiracil (FTD/TPI) plus bevacizumab in metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC).
Objective: This exploratory biomarker analysis of TRUSTY investigated the relationship between baseline plasma concentrations of angiogenesis-related factors and cell-free DNA (cfDNA), and the efficacy of FTD/TPI plus bevacizumab in patients with mCRC.
Patients and methods: The disease control rate (DCR) and progression-free survival (PFS) were compared between baseline plasma samples of patients with high and low plasma concentrations (based on the median value) of angiogenesis-related factors. Correlations between cfDNA concentrations and PFS were assessed.
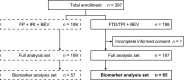
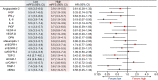
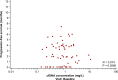
Results: Baseline characteristics (n = 65) were as follows: male/female, 35/30; median age, 64 (range 25-84) years; and RAS status wild-type/mutant, 29/36. Patients in the hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-low and interleukin (IL)-8-low groups had a significantly higher DCR (risk ratio [95% confidence intervals {CIs}]) than patients in the HGF-high (1.83 [1.12-2.98]) and IL-8-high (1.70 [1.02-2.82]) groups. PFS (hazard ratio {HR} [95% CI]) was significantly longer in patients in the HGF-low (0.33 [0.14-0.79]), IL-8-low (0.31 [0.14-0.70]), IL-6-low (0.19 [0.07-0.50]), osteopontin-low (0.39 [0.17-0.88]), thrombospondin-2-low (0.42 [0.18-0.98]), and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1-low (0.26 [0.10-0.67]) groups versus those having corresponding high plasma concentrations of these angiogenesis-related factors. No correlation was observed between cfDNA concentration and PFS.
Conclusion: Low baseline plasma concentrations of HGF and IL-8 may predict better DCR and PFS in patients with mCRC receiving FTD/TPI plus bevacizumab, however further studies are warranted.
Clinical trial registration number: jRCTs031180122.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors report support for the present manuscript (e.g., funding, provision of study materials, medical writing, and article processing charges) from Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd K.K. Mitsuru Yokota, Hitoshi Ojima, Naotoshi Sugimoto, Yasushi Tsuji, and Soichiro Ishihara have no other conflicts of interest. Yu Sunakawa has received institutional grants or contracts from Chugai, Taiho, Takeda, Otsuka, and Eli Lilly Japan; payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speaker’s bureau, manuscript writing, or educational events from Eli Lilly Japan, Bristol Myers Squibb, Chugai, Takeda, Ono, Merck Biopharma, Taiho, Bayer, Daiichi Sankyo, MSD, Sysmex, and Guardant Health; and has participated on the data safety monitoring board or advisory board of Merck Biopharma, Ono, and Guardant Health. Yasutoshi Kuboki has received institutional grants or contracts from Taiho, Takeda, Ono, AbbVie, Janssen Oncology, Boehringer Ingelheim, Incyte, Amgen, Chugai, GlaxoSmithKline, Genmab, Astellas, Daiichi Sankyo, and Eli Lilly Japan; personal consulting fees from Amgen, Takeda, and Boehringer Ingelheim; and payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speaker’s bureau, manuscript writing, or educational events from Taiho, Ono, Bayer, Eli Lilly Japan, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Merck Serono. Jun Watanabe has received institutional grants or contracts from Medtronic, Amco, and Terumo; and payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speaker’s bureau, manuscript writing, or educational events from Medtronic, Johnson & Johnson, Eli Lilly Japan, and Takeda. Tetsuji Terazawa has received consulting fees from Chugai, Eli Lilly Japan, Taiho, and Sanofi; has been part of the data safety monitoring board or advisory board of Sanofi; and is an employee of Shionogi. Hisato Kawakami has received institutional grants or contracts from Eisai, Kobayashi, and Bristol Myers Squibb; personal consulting fees from Daiichi Sankyo; and payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speaker’s bureau, manuscript writing, or educational events from Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly Japan, Ono, Daiichi Sankyo, Takeda, Teijin, Otsuka, Bayer, MSD, Chugai, Merck Biopharma, Yakult, and Taiho. Masato Nakamura has received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speaker’s bureau, manuscript writing, or educational events from Eli Lilly Japan, Nihon Servier, Daiichi Sankyo, Ono, Taiho, Yakult, Merck & Co., Bayer, Chugai, Merck Biopharma, Otsuka, Takeda, and AstraZeneca. Masahito Kotaka has received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speaker’s bureau, manuscript writing, or educational events from Chugai, Takeda, Taiho, Yakult, and Eli Lilly Japan. Eiji Oki has received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speaker’s bureau, manuscript writing, or educational events from Taiho, Takeda, Chugai, Bristol Myers Squibb, Bayer, Eli Lilly Japan, and Ono. Takeshi Kajiwara has received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speaker’s bureau, manuscript writing, or educational events from Chugail, Eli Lilly Japan, Bristol Myers Squibb, Taiho, and Ono. Yoshiyuki Yamamoto has received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speaker’s bureau, manuscript writing, or educational events from Ono, Bristol Myers Squibb, Yakult, Chugai, Eli Lilly Japan, Bayer, Taiho, Servier, Takeda, Daiichi Sankyo, AstraZeneca, and Insight. Tadamichi Denda has received institutional grants or contracts from Ono, MSD, Bristol Myers Squibb Foundation, Amgen, and Pfizer; and payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speaker’s bureau, manuscript writing, or educational events from Daiichi Sankyo, Sysmex, and Ono. Takao Tamura has received institutional grants or contracts from Chugai, Ltd; and payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speaker’s bureau, manuscript writing, or educational events from Takeda, Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Bristol Myers Squibb, Ono, and Chugai. Hiroya Taniguchi has received institutional grants or contracts from Takeda, Daiichi Sankyo, and Ono; and payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speaker’s bureau, manuscript writing, or educational events from Takeda, Ono, Eli Lilly Japan, Merck Biopharma, and Chugai. Takako Eguchi Nakajima has received institutional grants or contracts from Guardant Health, Taiho, Takeda, Chugai, Nippon Kayaku Co., AbbVie, Eli Lilly Japan, Shionogi, Otsuka, and Taisho; and payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speaker’s bureau, manuscript writing, or educational events from Sumitomo Dainippon, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Ono, Taiho, Amgen, Takeda, Chugai, Sanofi, Novartis Japan, Daiichi Sankyo, AstraZeneca, IQVIA, GlaxoSmithKline, NOBEL Pharma, and Parexel. Satoshi Morita has received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speaker’s bureau, manuscript writing, or educational events from Bristol Myers Squibb, Chugai, Taiho, Eli Lilly Japan, and AstraZeneca. Kuniaki Shirao has received institutional grants or contracts from Ono. Naruhito Takenaka and Daisuke Ozawa are employees of Taiho. Takayuki Yoshino has received institutional grants or contracts from Amgen K.K., Chugai, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Falco Biosystems Ltd, Genomedia Inc., Molecular Health GmbH, MSD, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim, Ono, Pfizer Japan Inc., Roche Diagnostics K.K., Sanofi, Sysmex, and Taiho; personal consulting fees from Sumitomo Corporation; and payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speaker’s bureau, manuscript writing, or educational events from Bayer, Chugai, Merck Biopharma, MSD, Ono, and Takeda.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Phase II Study of FOLFIRI Plus Ziv-Aflibercept After Trifluridine/Tipiracil Plus Bevacizumab in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: WJOG 11018G.Target Oncol. 2024 Mar;19(2):181-190. doi: 10.1007/s11523-024-01043-2. Epub 2024 Mar 1. Target Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38427280 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of KRASG12 mutations on survival with trifluridine/tipiracil plus bevacizumab in patients with refractory metastatic colorectal cancer: post hoc analysis of the phase III SUNLIGHT trial.ESMO Open. 2024 Mar;9(3):102945. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2024.102945. Epub 2024 Mar 11. ESMO Open. 2024. PMID: 38471240 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Trifluridine/Tipiracil Plus Bevacizumab for Vulnerable Patients With Pretreated Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Retrospective Study (WJOG14520G).Oncologist. 2024 Mar 4;29(3):e330-e336. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyad296. Oncologist. 2024. PMID: 37950903 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Trifluridine/Tipiracil plus Bevacizumab for the Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Evidence from Real-World Series.Curr Oncol. 2023 May 24;30(6):5227-5239. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30060397. Curr Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37366880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Trial Data Review of the Combination FTD/TPI + Bevacizumab in the Treatment Landscape of Unresectable Metastatic Colorectal Cancer.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2024 Oct;25(10):1312-1322. doi: 10.1007/s11864-024-01261-w. Epub 2024 Sep 26. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39325367 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Elucidating the role of angiogenesis-related genes in colorectal cancer: a multi-omics analysis.Front Oncol. 2024 Jun 19;14:1413273. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1413273. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38962272 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Treatment Strategies and Molecular Pathways in Resistance Mechanisms of Antiangiogenic Therapies in Glioblastoma.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Aug 27;16(17):2975. doi: 10.3390/cancers16172975. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Phase II Study of FOLFIRI Plus Ziv-Aflibercept After Trifluridine/Tipiracil Plus Bevacizumab in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: WJOG 11018G.Target Oncol. 2024 Mar;19(2):181-190. doi: 10.1007/s11523-024-01043-2. Epub 2024 Mar 1. Target Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38427280 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- NCCN Clinical Practice guidelines in Oncology: Colon Cancer. 2023. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/colon.pdf. Accessed 19 May 2023.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

