The LINC01176-miR-218-5p-IL-36G Network is Responsible for the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis by Promoting Inflammation
- PMID: 38193028
- PMCID: PMC10771785
- DOI: 10.2147/CCID.S444265
The LINC01176-miR-218-5p-IL-36G Network is Responsible for the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis by Promoting Inflammation
Abstract
Purpose: Psoriasis is an incurable chronic inflammatory skin disease. The exact function and regulatory mechanism of non-coding RNA upregulation in psoriasis remains to be elucidated. The aim of this study was to analyse the role of the lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network of psoriasis and LINC01176 in the pathogenesis of psoriasis.
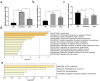
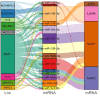
Patients and methods: We performed miRNA, lncRNA, and mRNA sequencing analysis in pretreatment and treatment psoriatic tissues and normal tissues, constructed an lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA coexpression network and screened mRNA-associated pathways using bioinformatics analysis. We further validated the regulatory role of LINC01176-miR-218-5p on the proliferation and inflammation of the psoriatic model by dual-luciferase reporter assay, cell transfection, CCK-8 method, TUNEL staining and animal model construction method. An lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA coexpression network was successfully constructed by RNA-seq data analysis.
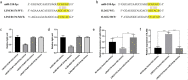
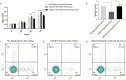
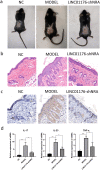
Results: We obtained the relationship between LINC01176, miR-218-5p and IL36-G. Analysis of the apoptotic and proliferative capacity of the transfected cells showed that miR-218-5p up-regulation significantly inhibited cell proliferation and promoted apoptosis. A mouse model of psoriasis was successfully established. Phenotypic observations revealed that keratin-forming cells in mice coated with LINC01176-shRNA emulsifier were significantly lower than those in the model group and close to those in the normal group. HE and immunohistochemical experiments were performed, and the results showed the role and mechanism of action of LINC01176-shRNA. Suppression of LINC01176 significantly inhibited the expression of IL-36G in psoriatic tissues. LINC01176 showed a targeting and positive correlation with IL36-G expression.
Conclusion: Our study shows that LINC01176 promotes the proliferation and invasion of keratinocytes and inhibits apoptosis by targeting miR-218-5p, which acts as a repressor of the psoriasis-associated IL-36G. The shRNA-LINC01176 emulsion showed potential treatment capability in alleviating symptoms of psoriasis.
Keywords: IL-36G; LINC01176; inflammation; psoriasis.
© 2024 Zhao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
LINC01176 Hinders Thyroid Cancer Progression by Sponging miR-146b-5p to Enhance SGIP1.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2023;23(13):1637-1648. doi: 10.2174/1871530323666230417083447. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2023. PMID: 37073140
-
Up-regulated lncRNA-MSX2P1 promotes the growth of IL-22-stimulated keratinocytes by inhibiting miR-6731-5p and activating S100A7.Exp Cell Res. 2018 Feb 15;363(2):243-254. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2018.01.014. Epub 2018 Jan 13. Exp Cell Res. 2018. PMID: 29339075
-
IL-22-induced miR-122-5p promotes keratinocyte proliferation by targeting Sprouty2.Exp Dermatol. 2017 Apr;26(4):368-374. doi: 10.1111/exd.13270. Exp Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 27943426
-
MiR-149-5p inhibits cell proliferation, promotes cell apoptosis and retards cell cycle of IL-22-stimulated HaCaT and NHEK keratinocytes via regulating PDE4D.Cytokine. 2023 Apr;164:156123. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2023.156123. Epub 2023 Feb 14. Cytokine. 2023. PMID: 36796259
-
LncRNA XIST Engages in Psoriasis via Sponging miR-338-5p to Regulate Keratinocyte Proliferation and Inflammation.Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2022;35(4):196-205. doi: 10.1159/000523781. Epub 2022 Mar 1. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35231918
Cited by
-
Role of FOXM1 and AURKB in regulating keratinocyte function in psoriasis.Open Med (Wars). 2024 Sep 30;19(1):20241049. doi: 10.1515/med-2024-1049. eCollection 2024. Open Med (Wars). 2024. PMID: 39381423 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Krueger G, Koo J, Fau - Lebwohl M, et al. The impact of psoriasis on quality of life: results of a 1998 national psoriasis foundation patient-membership survey. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137(3):280–284. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

