Teplizumab in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: An Updated Review
- PMID: 38187075
- PMCID: PMC10769466
- DOI: 10.17925/EE.2023.19.2.7
Teplizumab in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: An Updated Review
Abstract
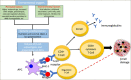
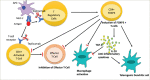
Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is a chronic autoimmune condition characterized by the irreversible destruction of the β cells of the pancreas, which leads to a lifelong dependency on exogenous insulin. Despite the advancements in insulin delivery methods, the suboptimal outcomes of these methods have triggered the search for therapies that may prevent or reverse the disease. Given the autoimmune aetiology of T1DM, therapies counteracting the immune-mediated destruction of the β-cells are the obvious target. Although several treatment strategies have been attempted to target cellular, humoral and innate immunity, very few have had a clinically meaningful impact. Of all the available immunomodulatory agents, cluster of differentiation (CD) 3 antibodies have exhibited the most promising preclinical and clinical results. Muromonab-CD3, which also happened to be a murine CD3 antibody, was the first monoclonal antibody approved for clinical use and was primarily indicated for graft rejection. The adverse effects associated with muromonab-CD3 led to its withdrawal. Teplizumab, a newer CD3 antibody, has a better side-effect profile because of its humanized nature and non-Fc-receptor-binding domain. In November 2022, teplizumab became the first immunomodulatory agent to be licensed by the US Food and Drug Administration for delaying the onset of T1DM in high-risk adults and children over 8 years old. The mechanism seems to be enhancing regulatory T-cell activity and promoting immune tolerance. This article reviews the mechanism of action and the clinical trials of teplizumab in individuals with T1DM or at risk of developing the disease.
Keywords: Anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody; immunomodulation; regulatory T cells; teplizumab; tolerance; type 1 diabetes mellitus.
© Touch Medical Media 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: Simran Thakkar, Aditi Chopra, Lakshmi Nagendra, Sanjay Kalra and Saptarshi Bhattacharya have no financial or non-financial relationships or activities to declare in relation to this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Teplizumab for treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus.Ann Pharmacother. 2012 Oct;46(10):1405-12. doi: 10.1345/aph.1R065. Epub 2012 Sep 11. Ann Pharmacother. 2012. PMID: 22968521 Review.
-
Teplizumab: type 1 diabetes mellitus preventable?Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2023 May;79(5):609-616. doi: 10.1007/s00228-023-03474-8. Epub 2023 Apr 1. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37004543 Review.
-
Safety and Efficacy of Teplizumab for Treatment of Type One Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2021;21(10):1895-1904. doi: 10.2174/1871530320999201209222921. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2021. PMID: 33302842
-
Journey of Teplizumab: A Promising Drug in the Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2024;21(1):e250124226249. doi: 10.2174/0115733998261825231026060241. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2024. PMID: 38279734 Review.
-
An Anti-CD3 Antibody, Teplizumab, in Relatives at Risk for Type 1 Diabetes.N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 15;381(7):603-613. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1902226. Epub 2019 Jun 9. N Engl J Med. 2019. PMID: 31180194 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
A Review of Stage 0 Biomarkers in Type 1 Diabetes: The Holy Grail of Early Detection and Prevention?J Pers Med. 2024 Aug 20;14(8):878. doi: 10.3390/jpm14080878. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 39202069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety of teplizumab in patients with high-risk for diabetes mellitus type 1: A systematic review.World J Diabetes. 2024 Aug 15;15(8):1793-1801. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i8.1793. World J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 39192866 Free PMC article.
-
Teplizumab's immunomodulatory effects on pancreatic β-cell function in type 1 diabetes mellitus.Clin Diabetes Endocrinol. 2024 Aug 10;10(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s40842-024-00181-w. Clin Diabetes Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 39123252 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources