TDP-43 chronic deficiency leads to dysregulation of transposable elements and gene expression by affecting R-loop and 5hmC crosstalk
- PMID: 38184854
- PMCID: PMC10857847
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113662
TDP-43 chronic deficiency leads to dysregulation of transposable elements and gene expression by affecting R-loop and 5hmC crosstalk
Abstract
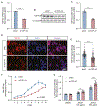
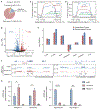
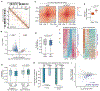
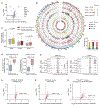
TDP-43 is an RNA/DNA-binding protein that forms aggregates in various brain disorders. TDP-43 engages in many aspects of RNA metabolism, but its molecular roles in regulating genes and transposable elements (TEs) have not been extensively explored. Chronic TDP-43 knockdown impairs cell proliferation and cellular responses to DNA damage. At the molecular level, TDP-43 chronic deficiency affects gene expression either locally or distally by concomitantly altering the crosstalk between R-loops and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) in gene bodies and long-range enhancer/promoter interactions. Furthermore, TDP-43 knockdown induces substantial disease-relevant TE activation by influencing their R-loop and 5hmC homeostasis in a locus-specific manner. Together, our findings highlight the genomic roles of TDP-43 in modulating R-loop-5hmC coordination in coding genes, distal regulatory elements, and TEs, presenting a general and broad molecular mechanism underlying the contributions of proteinopathies to the etiology of neurodegenerative disorders.
Keywords: CP: Neuroscience; DNA modification; R-loops; TDP-43; neurodegeneration; transposable element.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
TDP-43 dysfunction results in R-loop accumulation and DNA replication defects.J Cell Sci. 2020 Oct 30;133(20):jcs244129. doi: 10.1242/jcs.244129. J Cell Sci. 2020. PMID: 32989039 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulated Expression of Transposable Elements in TDP-43M337V Human Motor Neurons That Recapitulate Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis In Vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 19;23(24):16222. doi: 10.3390/ijms232416222. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555863 Free PMC article.
-
Transposable elements in TDP-43-mediated neurodegenerative disorders.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44099. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044099. Epub 2012 Sep 5. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22957047 Free PMC article.
-
Transposable elements as new players in neurodegenerative diseases.FEBS Lett. 2021 Nov;595(22):2733-2755. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14205. Epub 2021 Oct 18. FEBS Lett. 2021. PMID: 34626428 Review.
-
TDP-43 aggregation in neurodegeneration: are stress granules the key?Brain Res. 2012 Jun 26;1462:16-25. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.02.032. Epub 2012 Feb 22. Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22405725 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evolution of Repetitive Elements, Their Roles in Homeostasis and Human Disease, and Potential Therapeutic Applications.Biomolecules. 2024 Oct 2;14(10):1250. doi: 10.3390/biom14101250. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39456183 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Kwong LK, Truax AC, Micsenyi MC, Chou TT, Bruce J, Schuck T, Grossman M, Clark CM, et al. (2006). Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 314, 130–133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

