Drug repurposing: insights into the antimicrobial effects of AKBA against MRSA
- PMID: 38184513
- PMCID: PMC10771487
- DOI: 10.1186/s13568-024-01660-0
Drug repurposing: insights into the antimicrobial effects of AKBA against MRSA
Abstract
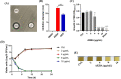
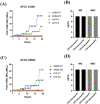
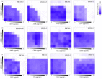
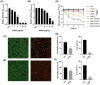
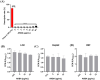
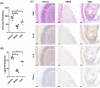
Staphylococcus aureus is a major threat in infectious diseases due to its varied infection types and increased resistance. S. aureus could form persister cells under certain condition and could also attach on medical apparatus to form biofilms, which exhibited extremely high resistance to antibiotics. 3-Acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid (AKBA) is a well-studied anti-tumor and antioxidant drug. This study is aimed to determine the antimicrobial effects of AKBA against S. aureus and its persister cells and biofilms. The in vitro antimicrobial susceptibility of AKBA was assessed by micro-dilution assay, disc diffusion assay and time-killing assay. Drug combination between AKBA and conventional antibiotics was detected by checkerboard assay. And the antibiofilm effects of AKBA against S. aureus were explored by crystal violet staining combined with SYTO/PI probes staining. Next, RBC lysis activity and CCK-8 kit were used to determine the cytotoxicity of AKBA. In addition, murine subcutaneous abscess model was used to assess the antimicrobial effects of AKBA in vivo. Our results revealed that AKBA was found to show effective antimicrobial activity against methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) with the minimal inhibitory concentration of 4-8 µg/mL with undetectable cytotoxicity. And no resistant mutation was induced by AKBA after 20 days of consecutive passage. Further, we found that AKBA could be synergy with gentamycin or amikacin against S. aureus and its clinical isolates. By crystal violet and SYTO9/PI staining, AKBA exhibited strong biofilm inhibitory and eradication effects at the concentration of 1 ~ 4 µg/mL. In addition, the effective antimicrobial effect was verified in vivo in a mouse model. And no detectable in vivo toxicity was found. These results indicated that AKBA has great potential to development as an alternative treatment for the refractory S. aureus infections.
Keywords: AKBA; Biofilm; Drug repurposing; Persister cells; Staphylococcus aureus.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antistaphylococcal and biofilm inhibitory activities of acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid from Boswellia serrata.BMC Microbiol. 2011 Mar 16;11:54. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-54. BMC Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21406118 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing CD5789 as an Antimicrobial Agent Against MRSA and Its High Resistant Phonotypes.Curr Microbiol. 2023 May 31;80(7):230. doi: 10.1007/s00284-023-03332-x. Curr Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37256372
-
Insights into the antimicrobial effects of ceritinib against Staphylococcus aureus in vitro and in vivo by cell membrane disruption.AMB Express. 2022 Nov 28;12(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s13568-022-01492-w. AMB Express. 2022. PMID: 36443539 Free PMC article.
-
Simeprevir restores the anti-Staphylococcus activity of polymyxins.AMB Express. 2023 Nov 2;13(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s13568-023-01634-8. AMB Express. 2023. PMID: 37917339 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial, Antibiofilm, and Anti-persister Activities of Penfluridol Against Staphylococcus aureus.Front Microbiol. 2021 Aug 18;12:727692. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.727692. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34489917 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ding Y, Qiao Y, Wang M, Zhang H, Li L, Zhang Y, Ge J, Song Y, Li Y, Wen A. Enhanced neuroprotection of acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid (AKBA)-loaded o-carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory pathways. Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53(6):3842–3853. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9333-9. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

