Differential miRNA Profiling Reveals miR-4433a-5p as a Key Regulator of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Progression via PIK3R2- mediated Phenotypic Modulation
- PMID: 38178680
- PMCID: PMC11348472
- DOI: 10.2174/0113862073243966231030093213
Differential miRNA Profiling Reveals miR-4433a-5p as a Key Regulator of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Progression via PIK3R2- mediated Phenotypic Modulation
Abstract
Objective: In this study, a high-throughput sequencing technology was used to screen the differentially expressed miRNA in the patients with "fast" and "slow" progression of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Moreover, the possible mechanism affecting the progression of COPD was preliminarily analyzed based on the target genes of candidate miRNAs.
Methods: The "fast" progressive COPD group included 6 cases, "slow" and Normal progressive COPD groups included 5 cases each, and COPD group included 3 cases. The peripheral blood samples were taken from the participants, followed by total RNA extraction and high throughput miRNA sequencing. The differentially expressed miRNAs among the progressive COPD groups were identified using bioinformatics analysis. Then, the candidate miRNAs were externally verified. In addition, the target gene of this miRNA was identified, and its effects on cell activity, cell cycle, apoptosis, and other biological phenotypes of COPD were analyzed.
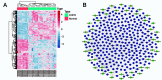
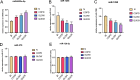
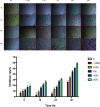
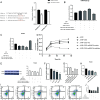
Results: Compared to the Normal group, a total of 35, 16, and 7 differentially expressed miRNAs were identified in the "fast" progressive COPD, "slow" progressive COPD group, and COPD group, respectively. The results were further confirmed using dual-luciferase reporter assay and transfection tests with phosphoinositide- 3-kinase, regulatory subunit 2 (PIK3R2) as a target gene of miR-4433a-5p; the result showed a negative regulatory correlation between the miRNA and its target gene. The phenotype detection showed that the activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) signaling pathway might participate in the progression of COPD by promoting the proliferation of inflammatory A549 cells and inhibiting cellular apoptosis.
Conclusions: MiR-4433a-5p can be used as a marker and potential therapeutic target for the progression of COPD. As a target gene of miR-4433a-5p, PIK3R2 can affect the progression of COPD by regulating phenotypes, such as cellular proliferation and apoptosis.
Keywords: COPD; biological phenotypes.; cell transfection; dual-luciferase reporter assay; miRNA; progressive development.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Expression of long non-coding RNA LUCAT1 in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and its potential functions in regulating cigarette smoke extract-induced 16HBE cell proliferation and apoptosis.J Clin Lab Anal. 2021 Jul;35(7):e23823. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23823. Epub 2021 Jun 14. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021. PMID: 34125980 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulated microRNA-135a ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis by inactivation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT signaling pathway via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit 2.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Aug;234(10):17663-17676. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28390. Epub 2019 Mar 25. J Cell Physiol. 2019. Retraction in: J Cell Physiol. 2022 Mar;237(3):2009. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30521 PMID: 30912120 Retracted.
-
Peripheral leukocyte microRNAs as novel biomarkers for COPD.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2017 Apr 6;12:1101-1112. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S130416. eCollection 2017. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2017. PMID: 28435243 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of Potential miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network in COPD Plasma by Bioinformatics Analysis.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2020 Sep 10;15:2135-2145. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S255262. eCollection 2020. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2020. PMID: 32982206 Free PMC article.
-
Ectopic expressed miR-203 contributes to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease via targeting TAK1 and PIK3CA.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Sep 1;8(9):10662-70. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26617776 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li F., Gao Z., Jing J., Xu D. Application of the Delphi method in the criterion of “fast”, “slow” development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Xinjiang Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2012;(10):43–45.
-
- Xu Q., Xu D., Li F. Delphi analysis on development speed of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. China Medical Herald. 2013;10(6):165–167.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

