S100A9 exerts insulin-independent antidiabetic and anti-inflammatory effects
- PMID: 38170783
- PMCID: PMC10796079
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adj4686
S100A9 exerts insulin-independent antidiabetic and anti-inflammatory effects
Abstract
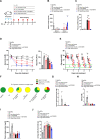
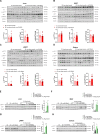
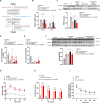
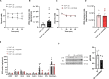
Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is characterized by insulin deficiency leading to hyperglycemia and several metabolic defects. Insulin therapy remains the cornerstone of T1DM management, yet it increases the risk of life-threatening hypoglycemia and the development of major comorbidities. Here, we report an insulin signaling-independent pathway able to improve glycemic control in T1DM rodents. Co-treatment with recombinant S100 calcium-binding protein A9 (S100A9) enabled increased adherence to glycemic targets with half as much insulin and without causing hypoglycemia. Mechanistically, we demonstrate that the hyperglycemia-suppressing action of S100A9 is due to a Toll-like receptor 4-dependent increase in glucose uptake in specific skeletal muscles (i.e., soleus and diaphragm). In addition, we found that T1DM mice have abnormal systemic inflammation, which is resolved by S100A9 therapy alone (or in combination with low insulin), hence uncovering a potent anti-inflammatory action of S100A9 in T1DM. In summary, our findings reveal the S100A9-TLR4 skeletal muscle axis as a promising therapeutic target for improving T1DM treatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hepatic non-parenchymal S100A9-TLR4-mTORC1 axis normalizes diabetic ketogenesis.Nat Commun. 2022 Jul 15;13(1):4107. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31803-5. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35840613 Free PMC article.
-
S100A9 extends lifespan in insulin deficiency.Nat Commun. 2019 Aug 7;10(1):3545. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11498-x. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31391467 Free PMC article.
-
Methods for insulin delivery and glucose monitoring in diabetes: summary of a comparative effectiveness review.J Manag Care Pharm. 2012 Aug;18(6 Suppl):S1-17. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2012.18.s6-a.1. J Manag Care Pharm. 2012. PMID: 22984955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deficiency of S100 calcium binding protein A9 attenuates vascular dysfunction in aged mice.Redox Biol. 2023 Jul;63:102721. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102721. Epub 2023 May 3. Redox Biol. 2023. PMID: 37163872 Free PMC article.
-
Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists in type 1 diabetes mellitus.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2019 Oct 15;76(21):1739-1748. doi: 10.1093/ajhp/zxz179. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2019. PMID: 31612934 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in the study of S100A9 in cardiovascular diseases.Cell Prolif. 2024 Aug;57(8):e13636. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13636. Epub 2024 Mar 19. Cell Prolif. 2024. PMID: 38504474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling the pathogenic interplay between SARS-CoV-2 and polycystic ovary syndrome using bioinformatics and experimental validation.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 2;14(1):22934. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74347-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39358491 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saeedi P., Petersohn I., Salpea P., Malanda B., Karuranga S., Unwin N., Colagiuri S., Guariguata L., Motala A. A., Ogurtsova K., Shaw J. E., Bright D., Williams R.; IDF Diabetes Atlas Committee , Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 157, 107843 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Wasserfall C., Nick H. S., Campbell-Thompson M., Beachy D., Haataja L., Kusmartseva I., Posgai A., Beery M., Rhodes C., Bonifacio E., Arvan P., Atkinson M., Persistence of pancreatic insulin mRNA expression and proinsulin protein in type 1 diabetes pancreata. Cell Metab. 26, 568–575.e3 (2017). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Quattrin T., Mastrandrea L. D., Walker L. S. K., Type 1 diabetes. Lancet 401, 2149–2162 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

