Pasteurized akkermansia muciniphila improves irritable bowel syndrome-like symptoms and related behavioral disorders in mice
- PMID: 38170633
- PMCID: PMC10766393
- DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2298026
Pasteurized akkermansia muciniphila improves irritable bowel syndrome-like symptoms and related behavioral disorders in mice
Abstract
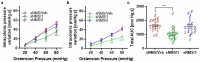
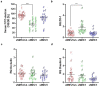
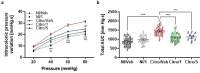
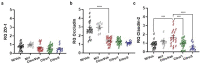
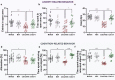
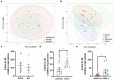
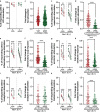
Gut - brain communications disorders in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) are associated with intestinal microbiota composition, increased gut permeability, and psychosocial disturbances. Symptoms of IBS are difficult to medicate, and hence much research is being made into alternative approaches. This study assesses the potential of a treatment with pasteurized Akkermansia muciniphila for alleviating IBS-like symptoms in two mouse models of IBS with different etiologies. Two clinically relevant animal models were used to mimic IBS-like symptoms in C57BL6/J mice: the neonatal maternal separation (NMS) paradigm and the Citrobacter rodentium infection model. In both models, gut permeability, colonic sensitivity, fecal microbiota composition and colonic IL-22 expression were evaluated. The cognitive performance and emotional state of the animals were also assessed by several tests in the C. rodentium infection model. The neuromodulation ability of pasteurized A. muciniphila was assessed on primary neuronal cells from mice dorsal root ganglia using a ratiometric calcium imaging approach. The administration of pasteurized A. muciniphila significantly reduced colonic hypersensitivity in both IBS mouse models, accompanied by a reinforcement of the intestinal barrier function. Beneficial effects of pasteurized A. muciniphila treatment have also been observed on anxiety-like behavior and memory defects in the C. rodentium infection model. Finally, a neuroinhibitory effect exerted by pasteurized A. muciniphila was observed on neuronal cells stimulated with two algogenic substances such as capsaicin and inflammatory soup. Our findings demonstrate novel anti-hyperalgesic and neuroinhibitory properties of pasteurized A. muciniphila, which therefore may have beneficial effects in relieving pain and anxiety in subjects with IBS.
Keywords: IBS; Pasteurized akkermansia muciniphila; anxiety-like disorders; colonic hypersensitivity; memory impairment; neuroinhibition.
Conflict of interest statement
P.D.C., W.M.dV. and A.B. are inventors on patent applications dealing with the use of specific bacteria and components in the treatment of different diseases. P.D.C. and W.M.dV. are co-founders of The Akkermansia Company SA. P.D.C. is co-founder of Enterosys. A.B., P.S. and W.M.dV. are employees of or associated with The Akkermansia Company. The other authors have declared no conflicting interest..
Figures

Similar articles
-
AhR/IL-22 pathway as new target for the treatment of post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome symptoms.Gut Microbes. 2022 Jan-Dec;14(1):2022997. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2021.2022997. Gut Microbes. 2022. PMID: 35090380 Free PMC article.
-
An Open-Labeled Study on Fecal Microbiota Transfer in Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients Reveals Improvement in Abdominal Pain Associated with the Relative Abundance of Akkermansia Muciniphila.Digestion. 2019;100(2):127-138. doi: 10.1159/000494252. Epub 2018 Nov 13. Digestion. 2019. PMID: 30423561
-
Live and pasteurized Akkermansia muciniphila ameliorates diabetic cognitive impairment by modulating gut microbiota and metabolites in db/db mice.Exp Neurol. 2024 Aug;378:114823. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.114823. Epub 2024 May 21. Exp Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38782351
-
Irritable bowel syndrome and gut microbiota.Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2020 Feb;27(1):28-35. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000523. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2020. PMID: 31789724 Review.
-
Akkermansia muciniphila: key player in metabolic and gastrointestinal disorders.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Sep;23(18):8075-8083. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201909_19024. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31599433 Review.
Cited by
-
The gut microbiome in disorders of gut-brain interaction.Gut Microbes. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2360233. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2360233. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Gut Microbes. 2024. PMID: 38949979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Traditional Chinese medicine for functional gastrointestinal disorders and inflammatory bowel disease: narrative review of the evidence and potential mechanisms involving the brain-gut axis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 17;15:1444922. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1444922. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39355776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the Mechanisms of Action of Akkermansia muciniphila in the Treatment of Non-Communicable Diseases.Nutrients. 2024 May 29;16(11):1695. doi: 10.3390/nu16111695. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38892628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut Microbiome Is Related to Cognitive Impairment in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients.Nutrients. 2024 Aug 12;16(16):2659. doi: 10.3390/nu16162659. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39203796 Free PMC article.
-
Akkermansia muciniphila: A promising probiotic against inflammation and metabolic disorders.Virulence. 2024 Dec;15(1):2375555. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2375555. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Virulence. 2024. PMID: 39192579 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
