The ubiquitin ligases Cbl and Cbl-b regulate macrophage growth by controlling CSF-1R import into macropinosomes
- PMID: 38170572
- PMCID: PMC10916879
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E23-09-0345
The ubiquitin ligases Cbl and Cbl-b regulate macrophage growth by controlling CSF-1R import into macropinosomes
Abstract
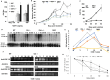
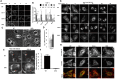
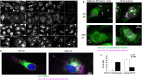
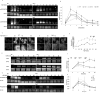
The ubiquitination of transmembrane receptors regulates endocytosis, intracellular traffic, and signal transduction. Bone marrow-derived macrophages from myeloid Cbl-/- and Cbl-b-/- double knockout (DKO) mice display sustained proliferation mirroring the myeloproliferative disease that these mice succumb to. Here, we found that the ubiquitin ligases Cbl and Cbl-b have overlapping functions for controlling the endocytosis and intracellular traffic of the CSF-1R. DKO macrophages displayed complete loss of ubiquitination of the CSF-1R whereas partial ubiquitination was observed for either single Cbl-/- or Cbl-b-/- macrophages. Unlike wild type, DKO macrophages were immortal and displayed slower CSF-1R internalization, elevated AKT signaling, and a failure to transport the CSF-1R into the lumen of nascent macropinosomes, leaving its cytoplasmic region available for signaling. CSF-1R degradation depended upon lysosomal vATPase activity in both WT and DKO macrophages, with this degradation confined to macropinosomes in WT but occurring in distributed/tubular lysosomes in DKO cells. RNA-sequencing comparison of Cbl-/-, Cbl-b-/- and DKO macrophages indicated that while the overall macrophage transcriptional program remained intact, DKO macrophages had alterations in gene expression associated with growth factor signaling, cell cycle, inflammation and senescence. Cbl-b-/- had minimal effect on the transcriptional program whereas Cbl-/- led to more alternations but only DKO macrophages demonstrated substantial changes in the transcriptome, suggesting overlapping but unique functions for the two Cbl-family members. Thus, Cbl/Cbl-b-mediated ubiquitination of CSF-1R regulates its endocytic fate, constrains inflammatory gene expression, and regulates signaling for macrophage proliferation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Cbl protooncoprotein stimulates CSF-1 receptor multiubiquitination and endocytosis, and attenuates macrophage proliferation.EMBO J. 1999 Jul 1;18(13):3616-28. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.13.3616. EMBO J. 1999. PMID: 10393178 Free PMC article.
-
Accumulation of c-Cbl and rapid termination of colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor signaling in interferon consensus sequence binding protein-deficient bone marrow-derived macrophages.Blood. 2002 May 1;99(9):3213-9. doi: 10.1182/blood.v99.9.3213. Blood. 2002. PMID: 11964285
-
A CSF-1 receptor phosphotyrosine 559 signaling pathway regulates receptor ubiquitination and tyrosine phosphorylation.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jan 14;286(2):952-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.166702. Epub 2010 Nov 1. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21041311 Free PMC article.
-
Biology and action of colony--stimulating factor-1.Mol Reprod Dev. 1997 Jan;46(1):4-10. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2795(199701)46:1<4::AID-MRD2>3.0.CO;2-V. Mol Reprod Dev. 1997. PMID: 8981357 Review.
-
Therapeutic applications of macrophage colony-stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1) and antagonists of CSF-1 receptor (CSF-1R) signaling.Blood. 2012 Feb 23;119(8):1810-20. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-09-379214. Epub 2011 Dec 20. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22186992 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

