Deficiency of Trex1 leads to spontaneous development of type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 38166933
- PMCID: PMC10763031
- DOI: 10.1186/s12986-023-00777-6
Deficiency of Trex1 leads to spontaneous development of type 1 diabetes
Abstract
Background: Type 1 diabetes is believed to be an autoimmune condition, characterized by destruction of insulin-producing cells, due to the detrimental inflammation in pancreas. Growing evidences have indicated the important role of type I interferon in the development of type 1 diabetes.
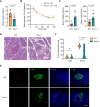
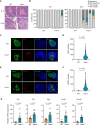
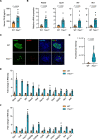
Methods: Trex1-deficient rats were generated by using CRISPR-Cas9. The fasting blood glucose level of rat was measured by a Roche Accuchek blood glucose monitor. The levels of insulin, islet autoantibodies, and interferon-β were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The inflammatory genes were detected by quantitative PCR and RNA-seq. Hematein-eosin staining was used to detect the pathological changes in pancreas, eye and kidney. The pathological features of kidney were also detected by Masson trichrome and periodic acid-Schiff staining. The distribution of islet cells, immune cells or ssDNA in pancreas was analyzed by immunofluorescent staining.
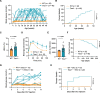
Results: In this study, we established a Trex1-deletion Sprague Dawley rat model, and unexpectedly, we found that the Trex1-/- rats spontaneously develop type 1 diabetes. Similar to human diabetes, the hyperglycemia in rats is accompanied by diabetic complications such as diabetic nephropathy and cataract. Mechanistical investigation revealed the accumulation of ssDNA and the excessive production of proinflammatory cytokines, including IFN-β, in Trex1 null pancreas. These are likely contributing to the inflammation in pancreas and eventually leading to the decline of pancreatic β cells.
Conclusions: Our study links the DNA-induced chronic inflammation to the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes, and also provides an animal model for type 1 diabetes studies.
Keywords: TREX1; Type 1 diabetes; Type I interferon.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effect of Electroacupuncture at "Weiwanxiashu" (EX-B 3) on Islet Morphology and the Expression of Pancreatic Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor in Type 2 Diabetes Rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2017 Apr 25;42(2):107-13. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2017. PMID: 29071956 Chinese.
-
Inflammatory status of the pancreas in NOD mice that do not develop overt diabetes.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2021 Jan-Mar;62(1):109-115. doi: 10.47162/RJME.62.1.10. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2021. PMID: 34609413 Free PMC article.
-
Transplantation of human dental pulp stem cells in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.Anat Sci Int. 2020 Sep;95(4):523-539. doi: 10.1007/s12565-020-00550-2. Epub 2020 May 31. Anat Sci Int. 2020. PMID: 32476103
-
18F-Labeled exendin(9-39).2012 Feb 9 [updated 2012 May 17]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2012 Feb 9 [updated 2012 May 17]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 22624171 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Pancreas Islet Transplantation for Patients With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Clinical Evidence Review.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2015 Sep 1;15(16):1-84. eCollection 2015. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2015. PMID: 26644812 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
From mechanism to therapy: the journey of CD24 in cancer.Front Immunol. 2024 May 31;15:1401528. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1401528. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38881902 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

