Dyslipidemia among HIV-infected patients in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38166636
- PMCID: PMC10763320
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-023-08910-9
Dyslipidemia among HIV-infected patients in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Dyslipidemia is responsible for more than half of the global ischemic heart disease (IHD) and more than 4 million deaths annually. Assessing the prevalence of dyslipidemia can be crucial in predicting the future disease development and possible intervention strategies. Therefore, this systematic review and meta-analysis was aimed at assessing the pooled prevalence of dyslipidemia in HIV-infected patients.
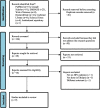
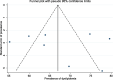
Methods: Electronic databases such as EMBASE, Google Scholar, PubMed, Web of Science, ResearchGate, Cochrane Library, and Science Direct were searched for articles and grey literature. All relevant studies found until our search period of May 24, 2023 were included. The Newcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale was used to assess the quality of the included studies. The data were extracted in Microsoft Excel. The STATA version 14 software was used to conduct the meta-analysis. I2 and Cochran's Q test were employed to assess the presence of heterogeneity between studies. Due to the presence of heterogeneity, a random effect model was used. The publication bias was assessed using the symmetry of the funnel plot and Egger's test statistics. Moreover, subgroup analysis, and sensitivity analysis were also done.
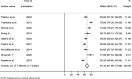
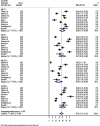
Results: A total of nine studies that reported the prevalence of dyslipidemia were included. The overall pooled prevalence of dyslipidemia among HIV-infected patients in Ethiopia was 67.32% (95% CI = 61.68%-72.96%). Furthermore, the overall pooled estimates of dyslipidemia among ART-taking and treatment-naïve HIV-infected patients were 69.74% (95% CI: 63.68-75.8, I2 = 87.2) and 61.46% (95% CI: 45.40-77.52, I2 = 90.3), respectively. Based on lipid profile fractionations, the pooled estimates for high total cholesterol (TC) were 39.08% (95% CI: 31.16-46.99), high triglycerides were 38.73% (95% CI: 28.58-48.88), high low density lipoprotein (LDL-c) was 28.40% (95% CI: 17.24-39.56), and low high density lipoprotein (HDL-c) was 39.42% (95% CI: 30.47-48.38).
Conclusion: More than two-thirds of HIV-infected patients experienced dyslipidemia. Therefore, it's critical to regularly evaluate lipid alterations in HIV-infected patients in order to prevent the onset of atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular problems.
Keywords: Antiretroviral therapy; Dyslipidemia; Ethiopia; HIV/AIDS; Serum lipid abnormality.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Prevalence of hepatotoxicity among HIV-infected patients in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Infect Dis. 2022 Nov 9;22(1):826. doi: 10.1186/s12879-022-07838-w. BMC Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 36352398 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetic dyslipidemia and its predictors among people with diabetes in Ethiopia: systematic review and meta-analysis.Syst Rev. 2024 Jul 20;13(1):190. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02593-2. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39033198 Free PMC article.
-
The prevalence of vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2023 Aug 30;12(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s13756-023-01291-3. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2023. PMID: 37649060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Health related quality of life and its association with social support among people living with HIV/AIDS receiving antiretroviral therapy in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2022 May 8;20(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s12955-022-01985-z. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2022. PMID: 35527300 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

