Inhibition of a novel Dickkopf-1-LDL receptor-related proteins 5 and 6 axis prevents diabetic cardiomyopathy in mice
- PMID: 38152853
- PMCID: PMC10906985
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad842
Inhibition of a novel Dickkopf-1-LDL receptor-related proteins 5 and 6 axis prevents diabetic cardiomyopathy in mice
Abstract
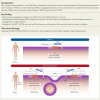
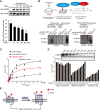
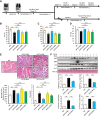
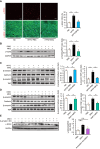
Background and aims: Anti-hypertensive agents are one of the most frequently used drugs worldwide. However, no blood pressure-lowering strategy is superior to placebo with respect to survival in diabetic hypertensive patients. Previous findings show that Wnt co-receptors LDL receptor-related proteins 5 and 6 (LRP5/6) can directly bind to several G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). Because angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) is the most important GPCR in regulating hypertension, this study examines the possible mechanistic association between LRP5/6 and their binding protein Dickkopf-1 (DKK1) and activation of the AT1R and further hypothesizes that the LRP5/6-GPCR interaction may affect hypertension and potentiate cardiac impairment in the setting of diabetes.
Methods: The roles of serum DKK1 and DKK1-LRP5/6 signalling in diabetic injuries were investigated in human and diabetic mice.
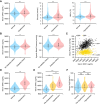
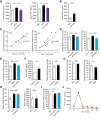
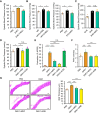
Results: Blood pressure up-regulation positively correlated with serum DKK1 elevations in humans. Notably, LRP5/6 physically and functionally interacted with AT1R. The loss of membrane LRP5/6 caused by injection of a recombinant DKK1 protein or conditional LRP5/6 deletions resulted in AT1R activation and hypertension, as well as β-arrestin1 activation and cardiac impairment, possibly because of multiple GPCR alterations. Importantly, unlike commonly used anti-hypertensive agents, administration of the anti-DKK1 neutralizing antibody effectively prevented diabetic cardiac impairment in mice.
Conclusions: These findings establish a novel DKK1-LRP5/6-GPCR pathway in inducing diabetic injuries and may resolve the long-standing conundrum as to why elevated blood DKK1 has deleterious effects. Thus, monitoring and therapeutic elimination of blood DKK1 may be a promising strategy to attenuate diabetic injuries.
Keywords: AngII/AT1R; DKK1; Diabetes; GPCR; Hypertension; LRP5/6; Metabolic syndrome; β-arrestin1.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Opposing Roles of Wnt Inhibitors IGFBP-4 and Dkk1 in Cardiac Ischemia by Differential Targeting of LRP5/6 and β-catenin.Circulation. 2016 Dec 13;134(24):1991-2007. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.024441. Epub 2016 Nov 1. Circulation. 2016. PMID: 27803037
-
A cell-based Dkk1 binding assay reveals roles for extracellular domains of LRP5 in Dkk1 interaction and highlights differences between wild-type and the high bone mass mutant LRP5(G171V).J Cell Biochem. 2009 Dec 1;108(5):1066-75. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22335. J Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19746449
-
Structure-based mutation analysis shows the importance of LRP5 beta-propeller 1 in modulating Dkk1-mediated inhibition of Wnt signaling.Gene. 2007 Apr 15;391(1-2):103-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2006.12.014. Epub 2006 Dec 29. Gene. 2007. PMID: 17276019
-
Pathogenic mutations and polymorphisms in the lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 reveal a new biological pathway for the control of bone mass.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2005 Apr;16(2):207-14. doi: 10.1097/01.mol.0000162326.62419.e4. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2005. PMID: 15767861 Review.
-
The role of Dickkopf-1 in bone development, homeostasis, and disease.Blood. 2009 Jan 15;113(3):517-25. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-03-145169. Epub 2008 Aug 7. Blood. 2009. PMID: 18687985 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endothelial Dickkopf-1 Promotes Smooth Muscle Cell-derived Foam Cell Formation via USP53-mediated Deubiquitination of SR-A During Atherosclerosis.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 May 19;20(8):2943-2964. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.91957. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38904030 Free PMC article.
References
-
- James PA, Oparil S, Carter BL, Cushman WC, Dennison-Himmelfarb C, Handler J, et al. . 2014 evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8). JAMA 2014;311:507–20. 10.1001/jama.2013.284427 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

