Roles and functions of IAV proteins in host immune evasion
- PMID: 38152399
- PMCID: PMC10751371
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1323560
Roles and functions of IAV proteins in host immune evasion
Abstract
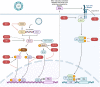
Influenza A viruses (IAVs) evade the immune system of the host by several regulatory mechanisms. Their genomes consist of eight single-stranded segments, including nonstructural proteins (NS), basic polymerase 1 (PB1), basic polymerase 2 (PB2), hemagglutinin (HA), acidic polymerase (PA), matrix (M), neuraminidase (NA), and nucleoprotein (NP). Some of these proteins are known to suppress host immune responses. In this review, we discuss the roles, functions and underlying strategies adopted by IAV proteins to escape the host immune system by targeting different proteins in the interferon (IFN) signaling pathway, such as tripartite motif containing 25 (TRIM25), inhibitor of nuclear factor κB kinase (IKK), mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein (MAVS), Janus kinase 1 (JAK1), type I interferon receptor (IFNAR1), interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3), IRF7, and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB). To date, the IAV proteins NS1, NS2, PB1, PB1-F2, PB2, HA, and PA have been well studied in terms of their roles in evading the host immune system. However, the detailed mechanisms of NS3, PB1-N40, PA-N155, PA-N182, PA-X, M42, NA, and NP have not been well studied with respect to their roles in immune evasion. Moreover, we also highlight the future perspectives of research on IAV proteins.
Keywords: IAV proteins; IAVs; IFNs; host immune system; immune evasion.
Copyright © 2023 Rashid, Xie, Li, Xie, Luo and Xie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hemagglutinin of Influenza A Virus Antagonizes Type I Interferon (IFN) Responses by Inducing Degradation of Type I IFN Receptor 1.J Virol. 2015 Dec 16;90(5):2403-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02749-15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26676772 Free PMC article.
-
Casein Kinase 1α Mediates the Degradation of Receptors for Type I and Type II Interferons Caused by Hemagglutinin of Influenza A Virus.J Virol. 2018 Mar 14;92(7):e00006-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00006-18. Print 2018 Apr 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29343571 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Innate Immune Responses by the Influenza A NS1 and PA-X Proteins.Viruses. 2018 Dec 12;10(12):708. doi: 10.3390/v10120708. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30545063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eukaryotic Translation Elongation Factor 1 Delta Inhibits the Nuclear Import of the Nucleoprotein and PA-PB1 Heterodimer of Influenza A Virus.J Virol. 2020 Dec 22;95(2):e01391-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01391-20. Print 2020 Dec 22. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 33087462 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Glycans and Non-glycans on the Epithelium and in the Immune System in H1-H18 Influenza A Virus Infections.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2556:205-242. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2635-1_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 36175637 Review.
Cited by
-
Host Innate Antiviral Response to Influenza A Virus Infection: From Viral Sensing to Antagonism and Escape.Pathogens. 2024 Jul 3;13(7):561. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13070561. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39057788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral Factors in Modulation of Host Immune Response: A Route to Novel Antiviral Agents and New Therapeutic Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 29;25(17):9408. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179408. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273355 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

