Rhotekin regulates axon regeneration through the talin-Vinculin-Vinexin axis in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 38150455
- PMCID: PMC10752531
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011089
Rhotekin regulates axon regeneration through the talin-Vinculin-Vinexin axis in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
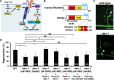
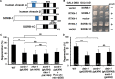
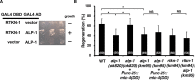
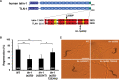
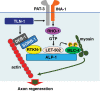
Axon regeneration requires actomyosin interaction, which generates contractile force and pulls the regenerating axon forward. In Caenorhabditis elegans, TLN-1/talin promotes axon regeneration through multiple down-stream events. One is the activation of the PAT-3/integrin-RHO-1/RhoA GTPase-LET-502/ROCK (Rho-associated coiled-coil kinase)-regulatory non-muscle myosin light-chain (MLC) phosphorylation signaling pathway, which is dependent on the MLC scaffolding protein ALP-1/ALP-Enigma. The other is mediated by the F-actin-binding protein DEB-1/vinculin and is independent of the MLC phosphorylation pathway. In this study, we identified the svh-7/rtkn-1 gene, encoding a homolog of the RhoA-binding protein Rhotekin, as a regulator of axon regeneration in motor neurons. However, we found that RTKN-1 does not function in the RhoA-ROCK-MLC phosphorylation pathway in the regulation of axon regeneration. We show that RTKN-1 interacts with ALP-1 and the vinculin-binding protein SORB-1/vinexin, and that SORB-1 acts with DEB-1 to promote axon regeneration. Thus, RTKN-1 links the DEB-1-SORB-1 complex to ALP-1 and physically connects phosphorylated MLC on ALP-1 to the actin cytoskeleton. These results suggest that TLN-1 signaling pathways coordinate MLC phosphorylation and recruitment of phosphorylated MLC to the actin cytoskeleton during axon regeneration.
Copyright: © 2023 Sakai et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The C. elegans BRCA2-ALP/Enigma Complex Regulates Axon Regeneration via a Rho GTPase-ROCK-MLC Phosphorylation Pathway.Cell Rep. 2018 Aug 14;24(7):1880-1889. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.07.049. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30110643
-
The Integrin Signaling Network Promotes Axon Regeneration via the Src-Ephexin-RhoA GTPase Signaling Axis.J Neurosci. 2021 Jun 2;41(22):4754-4767. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2456-20.2021. Epub 2021 May 7. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33963050 Free PMC article.
-
CDK14 Promotes Axon Regeneration by Regulating the Noncanonical Wnt Signaling Pathway in a Kinase-Independent Manner.J Neurosci. 2021 Oct 6;41(40):8309-8320. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0711-21.2021. Epub 2021 Aug 24. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34429379 Free PMC article.
-
Factors regulating axon regeneration via JNK MAP kinase in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Biochem. 2020 May 1;167(5):433-439. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvaa020. J Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32091576 Review.
-
Neural regeneration in Caenorhabditis elegans.Annu Rev Genet. 2012;46:499-513. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-110711-155550. Epub 2012 Sep 4. Annu Rev Genet. 2012. PMID: 22974301 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

