Cardiometabolic Risk Factors Associated With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Mechanistic Insight
- PMID: 38148756
- PMCID: PMC10750528
- DOI: 10.1177/11795514231220780
Cardiometabolic Risk Factors Associated With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Mechanistic Insight
Abstract
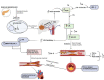
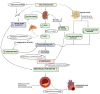
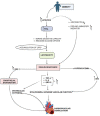
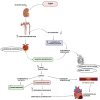
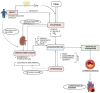
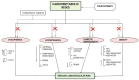
A complex metabolic condition referred to as Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is characterized by insulin resistance (IR) and decreased insulin production. Obesity, dyslipidemia, hypertension, and chronic inflammation are just a few of the cardiometabolic illnesses that people with T2DM are more likely to acquire and results in cardiovascular issues. It is essential to comprehend the mechanistic insights into these risk variables in order to prevent and manage cardiovascular problems in T2DM effectively. Impaired glycemic control leads to upregulation of De novo lipogenesis (DNL), promote hepatic triglyceride (TG) synthesis, worsening dyslipidemia that is accompanied by low levels of high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and high amounts of small, dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) further developing atherosclerosis. By causing endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and chronic inflammation, chronic hyperglycemia worsens already existing cardiometabolic risk factors. Vasoconstriction, inflammation, and platelet aggregation are caused by endothelial dysfunction, which is characterized by decreased nitric oxide production, increased release of vasoconstrictors, proinflammatory cytokines, and adhesion molecules. The loop of IR and endothelial dysfunction is sustained by chronic inflammation fueled by inflammatory mediators produced in adipose tissue. Infiltrating inflammatory cells exacerbate inflammation and the development of plaque in the artery wall. In addition, the combination of chronic inflammation, dyslipidemia, and IR contributes to the emergence of hypertension, a prevalent comorbidity in T2DM. The ability to target therapies and management techniques is made possible by improvements in our knowledge of these mechanistic insights. Aim of present review is to enhance our current understanding of the mechanistic insights into the cardiometabolic risk factors related to T2DM provides important details into the interaction of pathophysiological processes resulting in cardiovascular problems. Understanding these pathways will enable us to create efficient plans for the prevention, detection, and treatment of cardiovascular problems in T2DM patients, ultimately leading to better overall health outcomes.
Keywords: Type 2 diabetic mellitus (T2DM); cardiometabolic risk factors; cardiovascular diseases; diabetic nephropathy; dyslipidemia; hypertension; mortality; obesity.
Plain language summary
Understanding the factors that increase the risk of type 2 diabetes: Exploring how the body works Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a complex condition where the body struggles to use insulin properly and doesn’t produce enough of it. This often leads to other health issues like obesity, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and chronic inflammation. These problems increase the risk of heart and blood vessel diseases in people with T2DM. To tackle these issues effectively, it’s crucial to understand the underlying mechanisms. When blood sugar levels are not controlled, the body starts making more fat and storing it in the liver, leading to high triglycerides and low levels of good cholesterol. This process can block arteries, causing heart problems. High blood sugar also damages blood vessel linings, making them inflamed and less functional. This inflammation, combined with other factors like high cholesterol and insulin resistance, can lead to high blood pressure. Chronic inflammation, where the body’s defense system stays active for too long, worsens these problems. In T2DM, inflammation occurs in fat tissues, making the situation even worse. Inflammatory cells infiltrate blood vessel walls, promoting plaque buildup and further worsening heart issues. Understanding these processes helps us develop better strategies to prevent, detect, and treat heart problems in people with T2DM. By targeting these mechanisms, doctors can create more effective plans to improve the overall health of individuals with diabetes and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
© The Author(s) 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Pharmacological therapy of obesity].G Ital Cardiol (Rome). 2008 Apr;9(4 Suppl 1):83S-93S. G Ital Cardiol (Rome). 2008. PMID: 18773755 Italian.
-
Diabetic dyslipidemia.Am J Cardiol. 1998 Dec 17;82(12A):67U-73U; discussion 85U-86U. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(98)00848-0. Am J Cardiol. 1998. PMID: 9915665 Review.
-
Metabolic Dysregulation and Its Multifaceted Impact on Cardiovascular Autonomic Control in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Insights From Comprehensive Assessment.Cureus. 2024 May 7;16(5):e59776. doi: 10.7759/cureus.59776. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38846218 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond low-density lipoprotein: addressing the atherogenic lipid triad in type 2 diabetes mellitus and the metabolic syndrome.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2005;5(6):379-87. doi: 10.2165/00129784-200505060-00005. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2005. PMID: 16259526 Review.
-
Metabolic Syndrome in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Associated Microvascular Complications.Cureus. 2023 May 16;15(5):e39076. doi: 10.7759/cureus.39076. eCollection 2023 May. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37323312 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effect of boswellia (Boswellia serrata L.) supplementation on glycemic markers and lipid profile in type 2 diabetic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Clin Diabetes Healthc. 2024 Oct 10;5:1466408. doi: 10.3389/fcdhc.2024.1466408. eCollection 2024. Front Clin Diabetes Healthc. 2024. PMID: 39449720 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Melatonin: Beneficial Effects in Protecting against Heart Failure.Life (Basel). 2024 Jan 5;14(1):88. doi: 10.3390/life14010088. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38255703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Residual Syntax score and percutaneous coronary intervention in diabetic patients with renal insufficiency.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Oct 15;16(10):5909-5922. doi: 10.62347/VGPJ3431. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39544740 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Role in Cardiovascular Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Mechanisms, Risk Factors, and Management.Cureus. 2024 Aug 21;16(8):e67428. doi: 10.7759/cureus.67428. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39310549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory Hematological Ratios in Adolescents with Mental Disorders: A Scoping Review.Consort Psychiatr. 2024 Jul 6;5(2):45-61. doi: 10.17816/CP15514. eCollection 2024. Consort Psychiatr. 2024. PMID: 39071999 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balakumar P, Maung-U K, Jagadeesh G. Prevalence and prevention of cardiovascular disease and diabetes mellitus. Pharmacol Res. 2016;113:600-609. - PubMed
-
- Dal Canto E, Ceriello A, Rydén L, et al.. Diabetes as a cardiovascular risk factor: an overview of global trends of macro and micro vascular complications. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2019;26:25-32. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

