SARS-CoV-2 Fusion Peptide Conjugated to a Tetravalent Dendrimer Selectively Inhibits Viral Infection
- PMID: 38140131
- PMCID: PMC10748278
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15122791
SARS-CoV-2 Fusion Peptide Conjugated to a Tetravalent Dendrimer Selectively Inhibits Viral Infection
Abstract
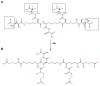
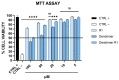
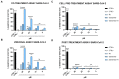
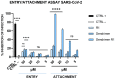
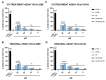
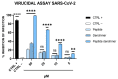
Fusion is a key event for enveloped viruses, through which viral and cell membranes come into close contact. This event is mediated by viral fusion proteins, which are divided into three structural and functional classes. The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike protein belongs to class I fusion proteins, characterized by a trimer of helical hairpins and an internal fusion peptide (FP), which is exposed once fusion occurs. Many efforts have been directed at finding antivirals capable of interfering with the fusion mechanism, mainly by designing peptides on the two heptad-repeat regions present in class I viral fusion proteins. Here, we aimed to evaluate the anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity of the FP sequence conjugated to a tetravalent dendrimer through a classical organic nucleophilic substitution reaction (SN2) using a synthetic bromoacetylated peptide mimicking the FP and a branched scaffold of poly-L-Lysine functionalized with cysteine residues. We found that the FP peptide conjugated to the dendrimer, unlike the monomeric FP sequence, has virucidal activity by impairing the attachment of SARS-CoV-2 to cells. Furthermore, we found that the peptide dendrimer does not have the same effects on other coronaviruses, demonstrating that it is selective against SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; dendrimer; fusion; fusion peptide; inhibitors; peptide; spike; viral fusion proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of the Fusion Peptide-Containing Region in Betacoronavirus Spike Glycoproteins.J Virol. 2016 May 27;90(12):5586-5600. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00015-16. Print 2016 Jun 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27030273 Free PMC article.
-
Kaempferol inhibits SARS-CoV-2 invasion by impairing heptad repeats-mediated viral fusion.Phytomedicine. 2023 Sep;118:154942. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154942. Epub 2023 Jun 23. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37421767 Free PMC article.
-
Ca2+ Ions Promote Fusion of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus with Host Cells and Increase Infectivity.J Virol. 2020 Jun 16;94(13):e00426-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00426-20. Print 2020 Jun 16. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32295925 Free PMC article.
-
Spike Glycoprotein Is Central to Coronavirus Pathogenesis-Parallel Between m-CoV and SARS-CoV-2.Ann Neurosci. 2021 Jul;28(3-4):201-218. doi: 10.1177/09727531211023755. Epub 2021 Oct 12. Ann Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 35341224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physiological and molecular triggers for SARS-CoV membrane fusion and entry into host cells.Virology. 2018 Apr;517:3-8. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2017.12.015. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Virology. 2018. PMID: 29275820 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO WHO Recommends Highly Successful COVID-19 Therapy and Calls for Wide Geographical Distribution and Transparency from Originator. [(accessed on 4 December 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/22-04-2022-who-recommends-highly-successfu....
-
- FDA FDA Approves First Oral Antiviral for Treatment of COVID-19 in Adults. [(accessed on 4 December 2023)]; Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-o....
-
- FDA Fact Sheet for Healthcare Providers: Emergency Use Authorization for Lagevrio™ (Molnupiravir) Capsules. [(accessed on 4 December 2023)]; Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/155054/download.
-
- Hedskog C., Rodriguez L., Roychoudhury P., Huang M.L., Jerome K.R., Hao L., Ireton R.C., Li J., Perry J.K., Han D., et al. Viral Resistance Analyses from the Remdesivir Phase 3 Adaptive COVID-19 Treatment Trial-1 (ACTT-1) J. Infect. Dis. 2023;228:1263–1273. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiad270. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- B63C22001230002/Campania FESR 2014/2020 "Realizzazione di Servizi di Ricerca e Sviluppo per la Lotta contro il COVID-19"
- 2017M8R7N9/PRIN 2017 "Natural and pharmacological inhibition of the early phase of viral replication (Vir-SudNet)"
- PE00000007, INF-ACT/EU funding within the NextGeneration EU-MUR PNRR Extended Partnership initiative on Emerging Infectious Diseases
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

