Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Metabolic Dysfunction Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD)
- PMID: 38139341
- PMCID: PMC10743953
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242417514
Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Metabolic Dysfunction Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD)
Abstract
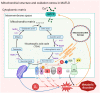
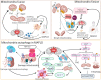
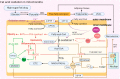
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become an increasingly common disease in Western countries and has become the major cause of liver cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in addition to viral hepatitis in recent decades. Furthermore, studies have shown that NAFLD is inextricably linked to the development of extrahepatic diseases. However, there is currently no effective treatment to cure NAFLD. In addition, in 2020, NAFLD was renamed metabolic dysfunction fatty liver disease (MAFLD) to show that its pathogenesis is closely related to metabolic disorders. Recent studies have reported that the development of MAFLD is inextricably associated with mitochondrial dysfunction in hepatocytes and hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). Simultaneously, mitochondrial stress caused by structural and functional disorders stimulates the occurrence and accumulation of fat and lipo-toxicity in hepatocytes and HSCs. In addition, the interaction between mitochondrial dysfunction and the liver-gut axis has also become a new point during the development of MAFLD. In this review, we summarize the effects of several potential treatment strategies for MAFLD, including antioxidants, reagents, and intestinal microorganisms and metabolites.
Keywords: MAFLD; fatty acid metabolism; liver–gut axis; mitochondrial antioxidant; mitochondrial quality control; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest exist in the review, and it was approved by all authors for publication. I would like to declare on behalf of my coauthors that the work described is original research that has not been published previously and is not under consideration for publication elsewhere, in whole or in part.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress in nonalcoholic (metabolic associated) fatty liver disease (NAFLD/MAFLD).J Cell Biochem. 2022 Oct;123(10):1585-1606. doi: 10.1002/jcb.30247. Epub 2022 May 1. J Cell Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35490371 Review.
-
Abnormal metabolism in hepatic stellate cells: Pandora's box of MAFLD related hepatocellular carcinoma.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2024 Mar;1879(2):189086. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2024.189086. Epub 2024 Feb 9. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38342420 Review.
-
Impact and usefulness of the transition to the new MAFLD classification for non-B, non-C HCC: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Gastroenterol. 2023 Jun 28;23(1):222. doi: 10.1186/s12876-023-02851-y. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37380950 Free PMC article.
-
The association between metabolic risk factors, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and the incidence of liver cancer: a nationwide population-based cohort study.Hepatol Int. 2022 Aug;16(4):807-816. doi: 10.1007/s12072-021-10281-9. Epub 2022 Jan 22. Hepatol Int. 2022. PMID: 35064545
-
Mitochondrial Dysfunction Plays Central Role in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 30;23(13):7280. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137280. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806284 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Can Nutraceuticals Support the Treatment of MASLD/MASH, and thus Affect the Process of Liver Fibrosis?Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 11;25(10):5238. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105238. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Underlying Mechanisms behind the Brain-Gut-Liver Axis and Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD): An Update.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 26;25(7):3694. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073694. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: The Influence of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Mitochondrial Dysfunctions, and the Role of Polyphenols.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Oct 10;17(10):1354. doi: 10.3390/ph17101354. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39458995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifaceted mitochondrial as a novel therapeutic target in dry eye: insights and interventions.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Sep 6;10(1):398. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02159-0. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 39242592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early monitoring values of oncogenic signalling molecules for hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Jun 15;16(6):2350-2361. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2350. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38994143 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Polyzos S.A., Chrysavgis L., Vachliotis I.D., Chartampilas E., Cholongitas E. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma:Insights in epidemiology, pathogenesis, imaging, prevention and therapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2023;93:20–35. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2023.04.010. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

