Prediction of Thermostability of Enzymes Based on the Amino Acid Index (AAindex) Database and Machine Learning
- PMID: 38138586
- PMCID: PMC10746113
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28248097
Prediction of Thermostability of Enzymes Based on the Amino Acid Index (AAindex) Database and Machine Learning
Abstract
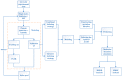
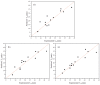
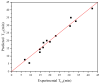
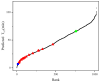
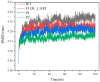
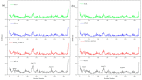
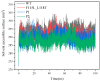
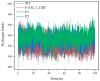
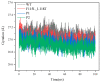
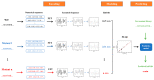
The combination of wet-lab experimental data on multi-site combinatorial mutations and machine learning is an innovative method in protein engineering. In this study, we used an innovative sequence-activity relationship (innov'SAR) methodology based on novel descriptors and digital signal processing (DSP) to construct a predictive model. In this paper, 21 experimental (R)-selective amine transaminases from Aspergillus terreus (AT-ATA) were used as an input to predict higher thermostability mutants than those predicted using the existing data. We successfully improved the coefficient of determination (R2) of the model from 0.66 to 0.92. In addition, root-mean-squared deviation (RMSD), root-mean-squared fluctuation (RMSF), solvent accessible surface area (SASA), hydrogen bonds, and the radius of gyration were estimated based on molecular dynamics simulations, and the differences between the predicted mutants and the wild-type (WT) were analyzed. The successful application of the innov'SAR algorithm in improving the thermostability of AT-ATA may help in directed evolutionary screening and open up new avenues for protein engineering.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; directed evolution; extended sequence; machine learning; molecular dynamics simulation; thermostability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Machine Learning Study on the Thermostability Prediction of (R)-ω-Selective Amine Transaminase from Aspergillus terreus.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Aug 16;2021:2593748. doi: 10.1155/2021/2593748. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34447850 Free PMC article.
-
[Deletion of a dynamic surface loop improves thermostability of (R)-selective amine transaminase from Aspergillus terreus].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2017 Dec 25;33(12):1923-1933. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.170279. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2017. PMID: 29271170 Chinese.
-
A machine learning approach for reliable prediction of amino acid interactions and its application in the directed evolution of enantioselective enzymes.Sci Rep. 2018 Nov 13;8(1):16757. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35033-y. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30425279 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning-assisted enzyme engineering.Methods Enzymol. 2020;643:281-315. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2020.05.005. Epub 2020 Jun 12. Methods Enzymol. 2020. PMID: 32896285 Review.
-
Data-driven strategies for the computational design of enzyme thermal stability: trends, perspectives, and prospects.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2023 Mar 25;55(3):343-355. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2023033. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2023. PMID: 37143326 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Reetz M.T. Directed Enzyme Evolution: Advances and Applications. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2017. Recent Advances in Directed Evolution of Stereoselective Enzymes; pp. 69–99. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

