Interspecies chimerism with human embryonic stem cells generates functional human dopamine neurons at low efficiency
- PMID: 38134925
- PMCID: PMC10828682
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2023.11.009
Interspecies chimerism with human embryonic stem cells generates functional human dopamine neurons at low efficiency
Abstract
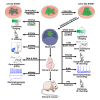
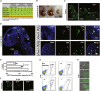
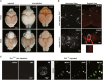
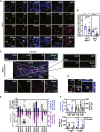
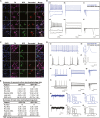
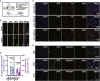
Interspecies chimeras offer great potential for regenerative medicine and the creation of human disease models. Whether human pluripotent stem cell-derived neurons in an interspecies chimera can differentiate into functional neurons and integrate into host neural circuity is not known. Here, we show, using Engrailed 1 (En1) as a development niche, that human naive-like embryonic stem cells (ESCs) can incorporate into embryonic and adult mouse brains. Human-derived neurons including tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)+ neurons integrate into the mouse brain at low efficiency. These TH+ neurons have electrophysiologic properties consistent with their human origin. In addition, these human-derived neurons in the mouse brain accumulate pathologic phosphorylated α-synuclein in response to α-synuclein preformed fibrils. Optimization of human/mouse chimeras could be used to study human neuronal differentiation and human brain disorders.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Generating functional cells through enhanced interspecies chimerism with human pluripotent stem cells.Stem Cell Reports. 2022 May 10;17(5):1059-1069. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2022.03.009. Epub 2022 Apr 14. Stem Cell Reports. 2022. PMID: 35427483 Free PMC article.
-
Improved cell therapy protocols for Parkinson's disease based on differentiation efficiency and safety of hESC-, hiPSC-, and non-human primate iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons.Stem Cells. 2013 Aug;31(8):1548-62. doi: 10.1002/stem.1415. Stem Cells. 2013. PMID: 23666606 Free PMC article.
-
Human-animal interspecies chimerism via blastocyst complementation: advances, challenges and perspectives: a narrative review.Stem Cell Investig. 2021 Oct 11;8:20. doi: 10.21037/sci-2020-074. eCollection 2021. Stem Cell Investig. 2021. PMID: 34815975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generation of Functional Organs Using a Cell-Competitive Niche in Intra- and Inter-species Rodent Chimeras.Cell Stem Cell. 2021 Jan 7;28(1):141-149.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2020.11.019. Epub 2020 Dec 28. Cell Stem Cell. 2021. PMID: 33373620 Free PMC article.
-
Generating Human Organs via Interspecies Chimera Formation: Advances and Barriers.Yale J Biol Med. 2018 Sep 21;91(3):333-342. eCollection 2018 Sep. Yale J Biol Med. 2018. PMID: 30258320 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging Landscape of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Senescence Mechanisms and Implications on Therapeutic Strategies.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024 Jul 17;7(8):2306-2325. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.4c00284. eCollection 2024 Aug 9. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39144566 Review.
References
-
- Das S., Koyano-Nakagawa N., Gafni O., Maeng G., Singh B.N., Rasmussen T., Pan X., Choi K.D., Mickelson D., Gong W., et al. Generation of human endothelium in pig embryos deficient in ETV2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020;38:297–302. - PubMed
-
- Gherbassi D., Simon H.H. The engrailed transcription factors and the mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons. J. Neural. Transm. Suppl. 2006;1:47–55. - PubMed
-
- Hanks M., Wurst W., Anson-Cartwright L., Auerbach A.B., Joyner A.L. Rescue of the En-1 mutant phenotype by replacement of En-1 with En-2. Science. 1995;269:679–682. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

