M6A demethylase ALKBH5 regulates FOXO1 mRNA stability and chemoresistance in triple-negative breast cancer
- PMID: 38104484
- PMCID: PMC10770627
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102993
M6A demethylase ALKBH5 regulates FOXO1 mRNA stability and chemoresistance in triple-negative breast cancer
Abstract
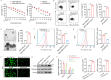
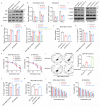
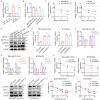
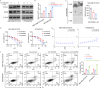
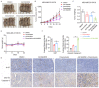
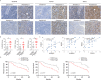
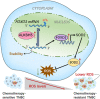
Resistance to chemotherapy is the main reason for treatment failure and poor prognosis in patients with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). Although the association of RNA N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modifications with therapy resistance is noticed, its role in the development of therapeutic resistance in TNBC is not well documented. This study aimed to investigate the potential mechanisms underlying reactive oxygen species (ROS) regulation in doxorubicin (DOX)-resistant TNBC. Here, we found that DOX-resistant TNBC cells displayed low ROS levels because of increased expression of superoxide dismutase (SOD2), thus maintaining cancer stem cells (CSCs) characteristics and DOX resistance. FOXO1 is a master regulator that reduces cellular ROS in DOX-resistant TNBC cells, and knockdown of FOXO1 significantly increased ROS levels by inhibiting SOD2 expression. Moreover, the m6A demethylase ALKBH5 promoted m6A demethylation of FOXO1 mRNA and increased FOXO1 mRNA stability in DOX-resistant TNBC cells. The analysis of clinical samples revealed that the increased expression levels of ALKBH5, FOXO1, and SOD2 were significantly positively correlated with chemoresistance and poor prognosis in patients with TNBC. To our knowledge, this is the first study to highlight that ALKBH5-mediated FOXO1 mRNA demethylation contributes to CSCs characteristics and DOX resistance in TNBC cells. Furthermore, pharmacological targeting of FOXO1 profoundly restored the response of DOX-resistant TNBC cells, both in vitro and in vivo. In conclusion, we demonstrated a critical function of ALKBH5-mediated m6A demethylation of FOXO1 mRNA in restoring redox balance, which in turn promoting CSCs characteristics and DOX resistance in TNBC, and suggested that targeting the ALKBH5/FOXO1 axis has therapeutic potential for patients with TNBC refractory to chemotherapy.
Keywords: ALKBH5; Chemoresistance; FOXO1; Reactive oxygen species; Triple-negative breast cancer.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of a novel mechanism for reversal of doxorubicin-induced chemotherapy resistance by TXNIP in triple-negative breast cancer via promoting reactive oxygen-mediated DNA damage.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Apr 12;13(4):338. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04783-z. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35414060 Free PMC article.
-
ALKBH5-Mediated m6A Demethylation of GLUT4 mRNA Promotes Glycolysis and Resistance to HER2-Targeted Therapy in Breast Cancer.Cancer Res. 2022 Nov 2;82(21):3974-3986. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-0800. Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36069931
-
ALKBH5-mediated m6A-demethylation of USP1 regulated T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell glucocorticoid resistance by Aurora B.Mol Carcinog. 2021 Sep;60(9):644-657. doi: 10.1002/mc.23330. Epub 2021 Jun 25. Mol Carcinog. 2021. PMID: 34169564
-
Post-translational modification of RNA m6A demethylase ALKBH5 regulates ROS-induced DNA damage response.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jun 4;49(10):5779-5797. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab415. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34048572 Free PMC article.
-
RNA demethylase ALKBH5 in cancer: from mechanisms to therapeutic potential.J Hematol Oncol. 2022 Jan 21;15(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01224-4. J Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35063010 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Potential Role of SNRPD1 Stabilized by IGF2BP2 in the Progression of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2024 Oct 11;16:679-688. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S481549. eCollection 2024. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2024. PMID: 39411513 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding the epitranscriptome: a new frontier for cancer therapy and drug resistance.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Oct 21;22(1):513. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01854-w. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39434167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in the Understanding of the Pathogenesis of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Cancer Med. 2024 Nov;13(22):e70410. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70410. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39558881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Writers, readers, and erasers RNA modifications and drug resistance in cancer.Mol Cancer. 2024 Aug 30;23(1):178. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02089-6. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39215288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N6-Methyladenosine methylation modification in breast cancer: current insights.J Transl Med. 2024 Oct 28;22(1):971. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05771-x. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39468547 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nolan E., Lindeman G.J., Visvader J.E. Deciphering breast cancer: from biology to the clinic. Cell. 2023;186:1708–1728. - PubMed
-
- Metzger O., Bozovic-Spasojevic I., Cardoso F. Treatment of metastatic breast cancer: an overview. EJHP Pract. 2011;17:20–23.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

