Baseline serum neurofilament light chain levels differentiate aggressive from benign forms of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a 20-year follow-up cohort
- PMID: 38085343
- PMCID: PMC10973070
- DOI: 10.1007/s00415-023-12135-w
Baseline serum neurofilament light chain levels differentiate aggressive from benign forms of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a 20-year follow-up cohort
Abstract
Background and objectives: Serum biomarkers are emerging as useful prognostic tools for multiple sclerosis (MS); however, long-term studies are lacking. We aimed to evaluate the long-term prognostic value of the serum levels of neurofilament light chain (NfL), total tau, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), and chitinase 3-like-1 (CHI3L1) measured close to the time of MS onset.
Methods: In this retrospective, exploratory, observational, case and controls study, patients with relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS) with available baseline serum samples and prospectively follow-up in our MS unit for a long time were selected based on their clinical evolution to form two groups: (1) a benign RRMS (bRRMS) group, defined as patients with an Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) score of ≤ 3 at ≥ 10 years of follow-up; (2) an aggressive RRMS (aRRMS) group, defined as patients with an EDSS score of ≥ 6 at ≤ 15 years of follow-up. An age-matched healthy control (HC) group was selected. NfL, total tau, and GFAP serum levels were quantified using a single-molecule array (SIMOA), and CHI3L1 was quantified using ELISA.
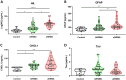
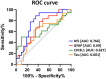
Results: Thirty-one patients with bRRMS, 19 with aRRMS, and 10 HC were included. The median follow-up time from sample collection was 17.74 years (interquartile range, 14.60-20.37). Bivariate and multivariate analyses revealed significantly higher NfL and GFAP levels in the aRRMS group than in the bRRMS group. A receiver operating characteristic curve analysis identified serum NfL level as the most efficient marker for distinguishing aRRMS from bRRMS.
Discussion: This proof-of-concept study comparing benign and aggressive RRMS groups reinforces the potential role of baseline NfL serum levels as a promising long-term disability prognostic marker. In contrast, serum GFAP, total tau, and CHI3L1 levels demonstrated a lower or no ability to differentiate between the long-term outcomes of RRMS.
Keywords: Biomarkers; CHI3L1; GFAP; Multiple sclerosis; Prognosis; sNfL.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Pablo Arroyo-Pereiro, Albert Muñoz-Vendrell, Isabel León, Antonio Martínez-Yélamos and Sergio Martínez-Yélamos received honoraria for participating on advisory boards and for collaborations as consultants and scientific communications; they also received research support as well as funding for travel and congress expenses from Roche, Biogen Idec, Novartis, TEVA, Merck, Genzyme, Sanofi, Bayer, Almirall, and Celgene. Pol Andrés-Benito received research support funding from Biogen Iberica S.L.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum GFAP and NfL levels in benign relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2021 Nov;56:103280. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2021.103280. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2021. PMID: 34627002
-
A Score Based on NfL and Glial Markers May Differentiate Between Relapsing-Remitting and Progressive MS Course.Front Neurol. 2020 Jul 16;11:608. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00608. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32765393 Free PMC article.
-
Early neurofilament light and glial fibrillary acidic protein levels improve predictive models of multiple sclerosis outcomes.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2023 Jun;74:104695. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2023.104695. Epub 2023 Apr 2. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2023. PMID: 37060852
-
Neurofilament light chain as a biomarker in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder: a comprehensive review and integrated analysis with glial fibrillary acidic protein.Neurol Sci. 2024 Mar;45(3):1255-1261. doi: 10.1007/s10072-023-07277-8. Epub 2023 Dec 23. Neurol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38141119 Review.
-
Blood Biomarkers as Prognostic Indicators for Neurological Injury in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 30;24(21):15738. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115738. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958721 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Global research trends on the links between NfL and neurological disorders: A bibliometric analysis and review.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 19;10(15):e34720. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34720. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39157316 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein as a Biomarker in Multiple Sclerosis and Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Jun 26;60(7):1050. doi: 10.3390/medicina60071050. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39064479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Value contribution of blood-based neurofilament light chain as a biomarker in multiple sclerosis using multi-criteria decision analysis.Front Public Health. 2024 Apr 22;12:1397845. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1397845. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38711771 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical trajectories of patients with multiple sclerosis from onset and their relationship with serum neurofilament light chain levels.Front Neurol. 2024 Oct 30;15:1477335. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1477335. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39539651 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

