The effects of semaphorin 3A in bone and cartilage metabolism: fundamental mechanism and clinical potential
- PMID: 38078001
- PMCID: PMC10701534
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1321151
The effects of semaphorin 3A in bone and cartilage metabolism: fundamental mechanism and clinical potential
Abstract
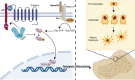
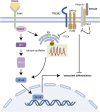
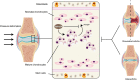
Semaphorin 3A (Sema3A) is a neuroinformatic protein molecule with widespread expression across various tissues and organs. Recent investigations have unveiled its pivotal role in the skeletal system, primarily through its binding interactions with two co-receptors, neuropilin-1 (Nrp-1) and members of the plexin family. Prior research has confirmed the expression of Sema3A and its receptors in both osteocytes and chondrocytes. Beyond its expression patterns, Sema3A plays a multifaceted role in regulating bone and cartilage metabolism via employing diverse signaling pathways. Additionally, it engages in collaborative interactions with the immune and nervous systems, contributing to the pathophysiological processes underlying a spectrum of bone and joint diseases. In this paper, we undertake a comprehensive review of recent research developments in this field. Our objective is to deepen the understanding of Sema3A within the context of skeletal physiology and pathology. Furthermore, we aim to furnish a valuable reference for potential therapeutic interventions in the realm of bone and joint diseases.
Keywords: bone; cartilage; metabolism; semaphorin 3A; tissue engineering.
Copyright © 2023 Wu, Huang and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Semaphorin 3A-Neuropilin-1 Signaling Modulates MMP13 Expression in Human Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 16;23(22):14180. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214180. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430655 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Semaphorin-3A and its receptors in endochondral ossification: potential role in skeletal development and innervation.Dev Dyn. 2005 Oct;234(2):393-403. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20512. Dev Dyn. 2005. PMID: 16145665
-
Semaphorin 3A is expressed in human osteoarthritic cartilage and antagonizes vascular endothelial growth factor 165-promoted chondrocyte migration: an implication for chondrocyte cloning.Arthritis Rheum. 2011 Oct;63(10):3000-9. doi: 10.1002/art.30482. Arthritis Rheum. 2011. PMID: 21953086
-
Emerging role of semaphorin-3A in autoimmune diseases.Inflammopharmacology. 2018 Jun;26(3):655-665. doi: 10.1007/s10787-018-0484-y. Epub 2018 Apr 25. Inflammopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29696565 Review.
-
Molecular basis of semaphorin-mediated axon guidance.J Neurobiol. 2000 Aug;44(2):219-29. doi: 10.1002/1097-4695(200008)44:2<219::aid-neu11>3.0.co;2-w. J Neurobiol. 2000. PMID: 10934324 Review.
Cited by
-
Neural regulation of mesenchymal stem cells in craniofacial bone: development, homeostasis and repair.Front Physiol. 2024 Jul 29;15:1423539. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1423539. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39135707 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Altman R., Asch E., Bloch D., Bole G., Borenstein D., Brandt K., et al. (1986). Development of criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis. Classification of osteoarthritis of the knee. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee of the American Rheumatism Association. Arthritis Rheum. 29, 1039–1049. 10.1002/art.1780290816 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

