Anti-inflammatory effect of dental pulp stem cells
- PMID: 38077342
- PMCID: PMC10701738
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1284868
Anti-inflammatory effect of dental pulp stem cells
Abstract
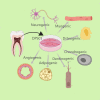
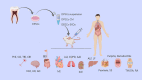
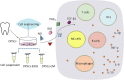
Dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) have received a lot of attention as a regenerative medicine tool with strong immunomodulatory capabilities. The excessive inflammatory response involves a variety of immune cells, cytokines, and has a considerable impact on tissue regeneration. The use of DPSCs for controlling inflammation for the purpose of treating inflammation-related diseases and autoimmune disorders such as supraspinal nerve inflammation, inflammation of the pulmonary airways, systemic lupus erythematosus, and diabetes mellitus is likely to be safer and more regenerative than traditional medicines. The mechanism of the anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of DPSCs is relatively complex, and it may be that they themselves or some of the substances they secrete regulate a variety of immune cells through inflammatory immune-related signaling pathways. Most of the current studies are still at the laboratory cellular level and animal model level, and it is believed that through the efforts of more researchers, DPSCs/SHED are expected to be transformed into excellent drugs for the clinical treatment of related diseases.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory; dental pulp stem cells; immune regulation; inflammation; regeneration.
Copyright © 2023 Li, Wang, Shi, Wu, Xing and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identifying Dental Pulp Stem Cell as a Novel Therapeutic trategy for Digestive Diseases.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024;19(10):1293-1302. doi: 10.2174/011574888X275737231120045815. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38018204 Review.
-
Immunomodulatory Mechanism and Potential Application of Dental Pulp-Derived Stem Cells in Immune-Mediated Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 29;24(9):8068. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098068. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Betamethasone suppresses the inflammatory response in LPS-stimulated dental pulp cells through inhibition of NF-κB.Arch Oral Biol. 2019 Feb;98:156-163. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2018.11.022. Epub 2018 Nov 20. Arch Oral Biol. 2019. PMID: 30500665
-
The Dental Pulp Stem/Progenitor Cells-Mediated Inflammatory-Regenerative Axis.Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2019 Oct;25(5):445-460. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2019.0106. Epub 2019 Sep 11. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2019. PMID: 31179893 Review.
-
Resolvin E1 accelerates pulp repair by regulating inflammation and stimulating dentin regeneration in dental pulp stem cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Jan 22;12(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02141-y. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33482900 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Role of Dental-derived Stem Cell-based Therapy and Their Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Post-COVID-19 Syndrome-induced Tissue Damage.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2024 Aug 16. doi: 10.1007/s12015-024-10770-y. Online ahead of print. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2024. PMID: 39150646 Review.
-
Combinatorial intervention with dental pulp stem cells and sulfasalazine in a rat model of ulcerative colitis.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Jul 29. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01532-w. Online ahead of print. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 39078564
-
A ROS-responsive hydrogel incorporated with dental follicle stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles promotes dental pulp repair by ameliorating oxidative stress.Bioact Mater. 2024 Jul 5;36:524-540. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.06.036. eCollection 2024 Jun. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 39072284 Free PMC article.
-
The potential therapeutic roles of dental pulp stem cells in spinal cord injury.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Apr 29;11:1363838. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1363838. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38741719 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li Y, Zhang M, Yang C, Zou D, Zhang Z. Advances in studies on biological properties and pre-clinicalapplication of dental pulp stem cells. Stomatology (2022) 42(01):1–7. doi: 10.13591/j.cnki.kqyx.2022.01.001 - DOI
-
- Sakai K, Yamamoto A, Matsubara K, Nakamura S, Naruse M, Yamagata M, et al. . Human dental pulp-derived stem cells promote locomotor recovery after complete transection of the rat spinal cord by multiple neuro-regenerative mechanisms. J Clin Invest (2012) 122(1):80–90. doi: 10.1172/jci59251 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Altanerova U, Benejova K, Altanerova V, Tyciakova S, Rychly B, Szomolanyi P, et al. . Dental pulp mesenchymal stem/stromal cells labeled with iron sucrose release exosomes and cells applied intra-nasally migrate to intracerebral glioblastoma. Neoplasma (2016) 63(6):925–33. doi: 10.4149/neo_2016_611 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

