Clinical and functional characterization of COL2A1 p.Gly444Ser variant: From a fetal phenotype to a previously undisclosed postnatal phenotype
- PMID: 38076483
- PMCID: PMC10698255
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bonr.2023.101728
Clinical and functional characterization of COL2A1 p.Gly444Ser variant: From a fetal phenotype to a previously undisclosed postnatal phenotype
Abstract
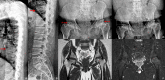
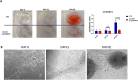
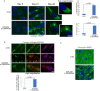
COL2A1 gene encodes the alpha-1 chain of type-II procollagen. Heterozygous pathogenic variants are associated with the broad clinical spectrum of genetic diseases known as type-II collagenopathies. We aimed to characterize the NM_001844.5:c.1330G>A;p.Gly444Ser variant detected in the COL2A1 gene through trio-based prenatal exome sequencing in a fetus presenting a severe skeletal phenotype at 31 Gestational Weeks and in his previously undisclosed mild-affected father. Functional studies on father's cutaneous fibroblasts, along with in silico protein modeling and in vitro chondrocytes differentiation, showed intracellular accumulation of collagen-II, its localization in external Golgi vesicles and nuclear morphological alterations. Extracellular matrix showed a disorganized fibronectin network. These results showed that p.Gly444Ser variant alters procollagen molecules processing and the assembly of mature type-II collagen fibrils, according to COL2A1-chain disorganization, displayed by protein modeling. Clinical assessment at 38 y.o., through a reverse-phenotyping approach, revealed limp gait, short and stocky appearance. X-Ray and MRI showed pelvis asymmetry with severe morpho-structural alterations of the femoral heads bilaterally, consistent with a mild form of type-II collagenopathy. This study shows how the fusion of genomics and clinical expertise can drive a diagnosis supported by cellular and bioinformatics studies to effectively establish variants pathogenicity.
Keywords: COL2A1; Exome sequencing; Functional characterization; Reverse-phenotyping; Type-II collagenopathies.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Short stature, platyspondyly, hip dysplasia, and retinal detachment: an atypical type II collagenopathy caused by a novel mutation in the C-propeptide region of COL2A1: a case report.BMC Med Genet. 2016 Dec 12;17(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s12881-016-0357-4. BMC Med Genet. 2016. PMID: 27955642 Free PMC article.
-
Parental somatogonadal COL2A1 mosaicism contributes to intrafamilial recurrence in a family with type 2 collagenopathy.Am J Med Genet A. 2020 Mar;182(3):454-460. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.61422. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Am J Med Genet A. 2020. PMID: 31854518
-
Identification and functional characteristics of a novel splicing heterozygote variant of COL2A1 associated with Stickler syndrome type I.Front Genet. 2024 Jul 10;15:1308737. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1308737. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 39050257 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated analysis of COL2A1 variant data and classification of type II collagenopathies.Clin Genet. 2020 Mar;97(3):383-395. doi: 10.1111/cge.13680. Epub 2019 Dec 6. Clin Genet. 2020. PMID: 31758797 Review.
-
Mutation Update for COL2A1 Gene Variants Associated with Type II Collagenopathies.Hum Mutat. 2016 Jan;37(1):7-15. doi: 10.1002/humu.22915. Epub 2015 Oct 21. Hum Mutat. 2016. PMID: 26443184 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

