Diagnostic efficacy of the triglyceride-glucose index in the prediction of contrast-induced nephropathy following percutaneous coronary intervention
- PMID: 38075076
- PMCID: PMC10703478
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1282675
Diagnostic efficacy of the triglyceride-glucose index in the prediction of contrast-induced nephropathy following percutaneous coronary intervention
Abstract
Introduction: Contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN) is a common complication of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Identifying patients at high CIN risk remains challenging. The triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index may help predict CIN but evidence is limited. We conducted a meta-analysis to evaluate the diagnostic value of TyG index for CIN after PCI.
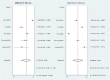
Methods: A systematic literature search was performed in MEDLINE, Cochrane, and EMBASE until August 2023 (PROSPERO registration: CRD42023452257). Observational studies examining TyG index for predicting CIN risk in PCI patients were included. This diagnostic meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the accuracy of the TyG index in predicting the likelihood of CIN. Secondary outcomes aimed to assess the pooled incidence of CIN and the association between an elevated TyG index and the risk of CIN.
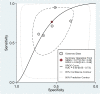
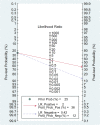
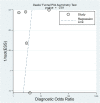
Results: Five studies (Turkey, n=2; China, n=3) with 3518 patients (age range: 57.6 to 68.22 years) were included. The pooled incidence of CIN was 15.3% [95% confidence interval (CI) 11-20.8%]. A high TyG index associated with increased CIN risk (odds ratio: 2.25, 95% CI 1.82-2.77). Pooled sensitivity and specificity were 0.77 (95% CI 0.59-0.88) and 0.55 (95% CI 0.43-0.68) respectively. Analysis of the summary receiver operating characteristic (sROC) curve revealed an area under the curve of 0.69 (95% CI 0.65-0.73). There was a low risk of publication bias (p = 0.81).
Conclusion: The TyG index displayed a noteworthy correlation with the risk of CIN subsequent to PCI. However, its overall diagnostic accuracy was found to be moderate in nature. While promising, the TyG index should not be used in isolation for CIN screening given the heterogeneity between studies. In addition, the findings cannot be considered conclusive given the scarcity of data. Further large-scale studies are warranted to validate TyG cutoffs and determine how to optimally incorporate it into current risk prediction models.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42023452257, identifier CRD42023452257.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; contrast-induced nephropathy; insulin resistance; meta-analysis; triglyceride-glucose index.
Copyright © 2023 Chang, Liu, Huang, Wu, Tsai, Hung, Chen and Feng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The triglyceride-glucose index and contrast-induced nephropathy in non-ST elevation myocardial infarction patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Jan 13;102(2):e32629. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032629. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 36637929 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of triglyceride-glucose index in patients with chronic coronary syndrome undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023 Nov 28;22(1):322. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-02060-7. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023. PMID: 38017540 Free PMC article.
-
Increased triglyceride-glucose index predicts contrast-induced nephropathy in non-diabetic NSTEMI patients: A prospective study.J Investig Med. 2023 Dec;71(8):838-844. doi: 10.1177/10815589231182317. Epub 2023 Jun 28. J Investig Med. 2023. PMID: 37377036
-
Association between the risk of hypertension and triglyceride glucose index in Chinese regions: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of a regional update.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Jul 31;10:1242035. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1242035. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37583585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Triglyceride-glucose index's link to cardiovascular outcomes post-percutaneous coronary intervention in China: a meta-analysis.ESC Heart Fail. 2024 Jun;11(3):1317-1328. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14679. Epub 2024 Jan 21. ESC Heart Fail. 2024. PMID: 38246749 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic and prognostic value of triglyceride glucose index: a comprehensive evaluation of meta-analysis.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Aug 23;23(1):310. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02392-y. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 39180024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Triglyceride-glucose index and health outcomes: an umbrella review of systematic reviews with meta-analyses of observational studies.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 May 23;23(1):177. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02241-y. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 38783270 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basta G, Chatzianagnostou K, Paradossi U, Botto N, Del Turco S, Taddei A, et al. . The prognostic impact of objective nutritional indices in elderly patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary coronary intervention. Int J Cardiol (2016) 221:987–92. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.07.039 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wi J, Ko YG, Kim JS, Kim BK, Choi D, Ha JW, et al. . Impact of contrast-induced acute kidney injury with transient or persistent renal dysfunction on long-term outcomes of patients with acute myocardial infarction undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Heart (2011) 97:1753–7. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2010.218677 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

