Determinants of neural tube defects among women who gave birth in hospitals in Eastern Ethiopia: evidence from a matched case control study
- PMID: 38071290
- PMCID: PMC10710723
- DOI: 10.1186/s12905-023-02796-0
Determinants of neural tube defects among women who gave birth in hospitals in Eastern Ethiopia: evidence from a matched case control study
Abstract
Introduction: Neural tube defects (NTDs) are severe birth defects caused by nutritional, genetic or environmental factors. Because NTDs continue to have a significant health and economic impact on children and community at large, it is crucial to investigate potential risk factors in order to develop novel approaches to NTDs prevention. Determinants for the development of NTDs differ by country, region as well as within the country. The objective of this study was to identify the determinants of NTDs among newborns delivered in three hospitals found in eastern Ethiopia.
Methods: A hospital-based matched case-control study was conducted among 138 cases and 138 control women who delivered in three teaching hospitals in Eastern Ethiopia in 2021. Data were collected using a structured and pre-tested interviewer-administered questionnaire. Cases were mothers who delivered a neonate with any type of NTDs regardless of gestational age or fetal viability, whereas controls were mothers who delivered an apparently healthy newborn. Chi-square was used to assess the significant difference between the two groups. Conditional logistic regression model was used to generate adjusted odds ratio with its corresponding 95% confidence intervals and compare the two groups.
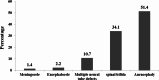
Results: Anencephaly (51.4%) and spinal bifida (34.1%) were the most frequently observed NTDs. None of study participants took preconception folic acid supplementation. Being a non-formal mothers (AOR = 0.34, 95% CI: 0.12-0.92, P = 0.034), rural residence, (AOR = 3.4, 95% CI: 1.18-9.78, P = 0.023), history of spontaneous abortion (AOR = 2.95, 95% CI: 1.15-7.55, P = 0.023), having severe anemia (AOR = 3.4, 95% CI: 1.17-9.87, P = 0.024), history of fever or cold (AOR = 2.75; 95% CI: 1.05-7.15, P = 0.038), and an exposure to various agro-chemicals (AOR = 3.39, 95% CI: 1.11-10.3, P = 0.032) were independent determinants of NTDs.
Conclusion and recommendation: In this study, NTDs were associated to several determinant factors in the area, including residential area, history of spontaneous abortion, severe anemia, fever/cold, antibiotic use before or during early pregnancy, and exposure to agrochemicals. Addressing the identified determinants is critical in averting the incidence of NTDs in the study area. Moreover, more research is needed to investigate women's dietary practices as well as the practice of preconception folic acid supplementation for pregnant women in Ethiopia's current health care system.
Keywords: Adjusted odds ratio; NTDs; Preconception folic acid; Predictive factors.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of periconceptional folic acid supplementation on the risk of neural tube defects associated with a previous spontaneous abortion or maternal first-trimester fever.Hum Reprod. 2019 Aug 1;34(8):1587-1594. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dez112. Hum Reprod. 2019. PMID: 31305926
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge of periconceptional folic acid supplementation and associated factors among pregnant women attending antenatal care at public health facilities in Hawassa, South Ethiopia.Birth Defects Res. 2023 Apr 1;115(6):647-657. doi: 10.1002/bdr2.2157. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Birth Defects Res. 2023. PMID: 36790035
-
Spina bifida and other neural tube defects.Curr Probl Pediatr. 2000 Nov-Dec;30(10):313-32. doi: 10.1067/mpp.2000.112052. Curr Probl Pediatr. 2000. PMID: 11147289 Review.
-
Neural tube defects: a review of global prevalence, causes, and primary prevention.Childs Nerv Syst. 2023 Jul;39(7):1703-1710. doi: 10.1007/s00381-023-05910-7. Epub 2023 Mar 8. Childs Nerv Syst. 2023. PMID: 36882610 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical