Unraveling the Intricacies of Autophagy and Mitophagy: Implications in Cancer Biology
- PMID: 38067169
- PMCID: PMC10706449
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12232742
Unraveling the Intricacies of Autophagy and Mitophagy: Implications in Cancer Biology
Abstract
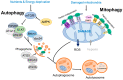
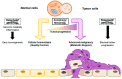
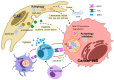
Autophagy is an essential lysosome-mediated degradation pathway that maintains cellular homeostasis and viability in response to various intra- and extracellular stresses. Mitophagy is a type of autophagy that is involved in the intricate removal of dysfunctional mitochondria during conditions of metabolic stress. In this review, we describe the multifaceted roles of autophagy and mitophagy in normal physiology and the field of cancer biology. Autophagy and mitophagy exhibit dual context-dependent roles in cancer development, acting as tumor suppressors and promoters. We also discuss the important role of autophagy and mitophagy within the cancer microenvironment and how autophagy and mitophagy influence tumor host-cell interactions to overcome metabolic deficiencies and sustain the activity of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) in a stromal environment. Finally, we explore the dynamic interplay between autophagy and the immune response in tumors, indicating their potential as immunomodulatory targets in cancer therapy. As the field of autophagy and mitophagy continues to evolve, this comprehensive review provides insights into their important roles in cancer and cancer microenvironment.
Keywords: autophagy; cancer; cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs); mitophagy; tumor microenvironment (TME); tumor-associated immune cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mitophagy in Cancer: A Tale of Adaptation.Cells. 2019 May 22;8(5):493. doi: 10.3390/cells8050493. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31121959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling the intricacies of cancer-associated fibroblasts: a comprehensive review on metabolic reprogramming and tumor microenvironment crosstalk.APMIS. 2024 Dec;132(12):906-927. doi: 10.1111/apm.13447. Epub 2024 Jun 14. APMIS. 2024. PMID: 38873945 Review.
-
Cigarette smoke metabolically promotes cancer, via autophagy and premature aging in the host stromal microenvironment.Cell Cycle. 2013 Mar 1;12(5):818-25. doi: 10.4161/cc.23722. Epub 2013 Feb 6. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23388463 Free PMC article.
-
Sirtuins' control of autophagy and mitophagy in cancer.Pharmacol Ther. 2021 May;221:107748. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107748. Epub 2020 Nov 24. Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33245993 Review.
-
A PINK1-mediated mitophagy pathway decides the fate of tumors-to be benign or malignant?Autophagy. 2018;14(4):563-566. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2018.1425057. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Autophagy. 2018. PMID: 29313453 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Anticancer Activity of Delta-Tocotrienol in Human Hepatocarcinoma: Involvement of Autophagy Induction.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jul 26;16(15):2654. doi: 10.3390/cancers16152654. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39123382 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer cell-selective induction of mitochondrial stress and immunogenic cell death by PT-112 in human prostate cell lines.J Transl Med. 2024 Oct 11;22(1):927. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05739-x. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39394618 Free PMC article.
-
Sex hormone-binding globulin promotes the osteogenic differentiation potential of equine adipose-derived stromal cells by activating the BMP signaling pathway.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Oct 17;15:1424873. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1424873. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39483986 Free PMC article.
-
Moderate-intensity aerobic exercise training improves CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes effector function by reducing mitochondrial loss.iScience. 2024 May 27;27(6):110121. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110121. eCollection 2024 Jun 21. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38957793 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

