The Major Hypotheses of Alzheimer's Disease: Related Nanotechnology-Based Approaches for Its Diagnosis and Treatment
- PMID: 38067098
- PMCID: PMC10705786
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12232669
The Major Hypotheses of Alzheimer's Disease: Related Nanotechnology-Based Approaches for Its Diagnosis and Treatment
Abstract
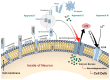
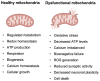
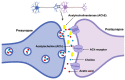
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a well-known chronic neurodegenerative disorder that leads to the progressive death of brain cells, resulting in memory loss and the loss of other critical body functions. In March 2019, one of the major pharmaceutical companies and its partners announced that currently, there is no drug to cure AD, and all clinical trials of the new ones have been cancelled, leaving many people without hope. However, despite the clear message and startling reality, the research continued. Finally, in the last two years, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first-ever medications to treat Alzheimer's, aducanumab and lecanemab. Despite researchers' support of this decision, there are serious concerns about their effectiveness and safety. The validation of aducanumab by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services is still pending, and lecanemab was authorized without considering data from the phase III trials. Furthermore, numerous reports suggest that patients have died when undergoing extended treatment. While there is evidence that aducanumab and lecanemab may provide some relief to those suffering from AD, their impact remains a topic of ongoing research and debate within the medical community. The fact is that even though there are considerable efforts regarding pharmacological treatment, no definitive cure for AD has been found yet. Nevertheless, it is strongly believed that modern nanotechnology holds promising solutions and effective clinical strategies for the development of diagnostic tools and treatments for AD. This review summarizes the major hallmarks of AD, its etiological mechanisms, and challenges. It explores existing diagnostic and therapeutic methods and the potential of nanotechnology-based approaches for recognizing and monitoring patients at risk of irreversible neuronal degeneration. Overall, it provides a broad overview for those interested in the evolving areas of clinical neuroscience, AD, and related nanotechnology. With further research and development, nanotechnology-based approaches may offer new solutions and hope for millions of people affected by this devastating disease.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; biomarkers; drug delivery; nanoparticles; nanotechnology; neurodegeneration; neuroscience.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Newer modalities in the management of Alzheimer's dementia along with the role of aducanumab and lecanemab in the treatment of its refractory cases.Dis Mon. 2023 May;69(5):101547. doi: 10.1016/j.disamonth.2023.101547. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Dis Mon. 2023. PMID: 36931947 Review.
-
Nanotechnology in the diagnostic and therapy for Alzheimer's disease.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2024 Mar;1868(3):130559. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2024.130559. Epub 2024 Jan 6. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2024. PMID: 38191034 Review.
-
High-clearance anti-amyloid immunotherapies in Alzheimer's disease. Part 2: putative scenarios and timeline in case of approval, recommendations for use, implementation, and ethical considerations in France.Rev Neurol (Paris). 2022 Dec;178(10):999-1010. doi: 10.1016/j.neurol.2022.08.002. Epub 2022 Nov 3. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2022. PMID: 36336488 Review.
-
Profiling lecanemab as a treatment option for Alzheimer's disease.Expert Rev Neurother. 2024 May;24(5):433-441. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2024.2333970. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Expert Rev Neurother. 2024. PMID: 38566584 Review.
-
Nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems for Alzheimer's disease management: Technical, industrial, and clinical challenges.J Control Release. 2017 Jan 10;245:95-107. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.11.025. Epub 2016 Nov 23. J Control Release. 2017. PMID: 27889394 Review.
Cited by
-
Transforming Healthcare with Nanomedicine: A SWOT Analysis of Drug Delivery Innovation.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Aug 5;18:3499-3521. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S470210. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39132625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A bibliometric and visual analysis of epigenetic research publications for Alzheimer's disease (2013-2023).Front Aging Neurosci. 2024 Jan 16;16:1332845. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1332845. eCollection 2024. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38292341 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

