Radiogenomic landscape: Assessment of specific phagocytosis regulators in lower-grade gliomas
- PMID: 38062999
- PMCID: PMC10903236
- DOI: 10.1177/15353702231211939
Radiogenomic landscape: Assessment of specific phagocytosis regulators in lower-grade gliomas
Abstract
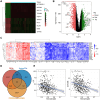
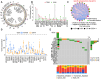
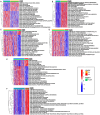
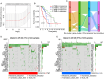
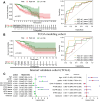
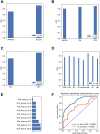
Genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screens have emerged as a powerful method for identifying key genes driving tumor growth. The aim of this study was to explore the phagocytosis regulators (PRs) specifically associated with lower-grade glioma (LGG) using the CRISPR-Cas9 screening database. Identifying these core PRs could lead to novel therapeutic targets and pave the way for a non-invasive radiogenomics approach to assess LGG patients' prognosis and treatment response. We selected 24 PRs that were overexpressed and lethal in LGG for analysis. The identified PR subtypes (PRsClusters, geneClusters, and PRs-score models) effectively predicted clinical outcomes in LGG patients. Immune response markers, such as CTLA4, were found to be significantly associated with PR-score. Nine radiogenomics models using various machine learning classifiers were constructed to uncover survival risk. The area under the curve (AUC) values for these models in the test and training datasets were 0.686 and 0.868, respectively. The CRISPR-Cas9 screen identified novel prognostic radiogenomics biomarkers that correlated well with the expression status of specific PR-related genes in LGG patients. These biomarkers successfully stratified patient survival outcomes and treatment response using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. This study has important implications for the development of precise clinical treatment strategies and holds promise for more accurate therapeutic approaches for LGG patients in the future.
Keywords: CRISPR-cas9; lower-grade glioma; phagocytosis regulators; prognostic; radiogenomics.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comprehensive Analysis of Phagocytosis-Related Regulators to Aid Prognostic Prediction and Immunotherapy in Patients with Low-Grade Glioma.Dis Markers. 2022 Apr 12;2022:4142684. doi: 10.1155/2022/4142684. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35510040 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR-cas9 screening identified lethal genes enriched in Hippo kinase pathway and of predictive significance in primary low-grade glioma.Mol Med. 2023 May 14;29(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s10020-023-00652-3. Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37183261 Free PMC article.
-
SHOX2 is a Potent Independent Biomarker to Predict Survival of WHO Grade II-III Diffuse Gliomas.EBioMedicine. 2016 Nov;13:80-89. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.10.040. Epub 2016 Oct 28. EBioMedicine. 2016. PMID: 27840009 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel cuproptosis-related gene signature and integrative analyses in patients with lower-grade gliomas.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 15;13:933973. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.933973. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36045691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical modeling of lower-grade gliomas.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 27;13:1139383. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1139383. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37051530 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gargini R, Segura-Collar B, Herránz B, García-Escudero V, Romero-Bravo A, Núñez FJ, García-Pérez D, Gutiérrez-Guamán J, Ayuso-Sacido A, Seoane J, Pérez-Núñez A, Sepúlveda-Sánchez JM, Hernández-Laín A, Castro MG, García-Escudero R, Ávila J, Sánchez-Gómez P. The IDH-TAU-EGFR triad defines the neovascular landscape of diffuse gliomas. Sci Transl Med 2020;12:eaax1501 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

