Prognostic significance and immune characteristics of APOE in gastric cancer
- PMID: 38054821
- PMCID: PMC10756126
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.205265
Prognostic significance and immune characteristics of APOE in gastric cancer
Abstract
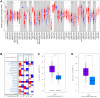
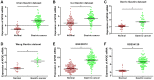
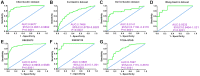
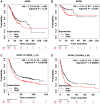
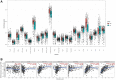
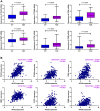
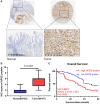
Gastric cancer (GC) is a prevalent malignancy affecting the digestive system, and it is the second leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide. Immunotherapy presents a potential lifeline for patients with advanced gastric cancer, emphasizing the need to find new molecular targets that improve the response to immunotherapy. In our research, we conducted a comprehensive bioinformatic analysis to investigate the expression profiles of apolipoprotein E (APOE) transcription. Subsequently, we examined the correlation between APOE transcription and the prognosis of GC patients. Additionally, we evaluated the connection between APOE transcription and immune cells abundance. To validate our findings, we conducted immunohistochemistry experiment to ascertain the level of APOE protein in GC patients and assessed its prognostic role in a cohort of 97 GC individuals. Our results revealed that APOE is increased in GC tissues, and APOE displays diagnostic potential in distinguishing GC from normal tissues. Notably, upregulated APOE expression in GC patients is associated with unfavorable overall survival. Differential APOE expression was further observed across different immune subtypes of GC, indicating its involvement in immune cell activation and infiltration. Moreover, we detected increased APOE protein expression in GC tissues, which exhibited a strong correlation with poor survival outcomes. In light of these findings, APOE has become a crucial prognostic molecular with immunomodulatory function in GC. These results underscore the significance of APOE across various cancer types, including GC, and provide valuable insights into its role from both a bioinformatics and clinical perspective.
Keywords: APOE; biomarker; gastric cancer; immunotherapy; prognostic; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prognostic significance and immune characteristics of GPR27 in gastric cancer.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Sep 12;15(17):9144-9166. doi: 10.18632/aging.205023. Epub 2023 Sep 12. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 37702614 Free PMC article.
-
Microarray profile analysis identifies ETS1 as potential biomarker regulated by miR-23b and modulates TCF4 in gastric cancer.World J Surg Oncol. 2021 Oct 23;19(1):311. doi: 10.1186/s12957-021-02417-w. World J Surg Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34686186 Free PMC article.
-
B7-H3 and CD47 co-expression in gastric cancer is a predictor of poor prognosis and potential targets for future dual-targeting immunotherapy.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Dec;149(18):16609-16621. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05408-4. Epub 2023 Sep 16. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37715830
-
Identification of Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers for Gastric Cancer Based on Bioinformatic Analysis.J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2023;42(4):61-68. doi: 10.1615/JEnvironPatholToxicolOncol.2023047804. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37522568
-
A novel necroptosis-related gene index for predicting prognosis and a cold tumor immune microenvironment in stomach adenocarcinoma.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 27;13:968165. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.968165. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36389725 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang FH, Zhang XT, Li YF, Tang L, Qu XJ, Ying JE, Zhang J, Sun LY, Lin RB, Qiu H, Wang C, Qiu MZ, Cai MY, et al.. The Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology (CSCO): Clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of gastric cancer, 2021. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2021; 41:747–95. 10.1002/cac2.12193 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

