CpG 684: an effective adjuvant for the inactivated COVID-19 vaccine in mice
- PMID: 38051998
- PMCID: PMC10241461
- DOI: 10.2217/fvl-2022-0172
CpG 684: an effective adjuvant for the inactivated COVID-19 vaccine in mice
Abstract
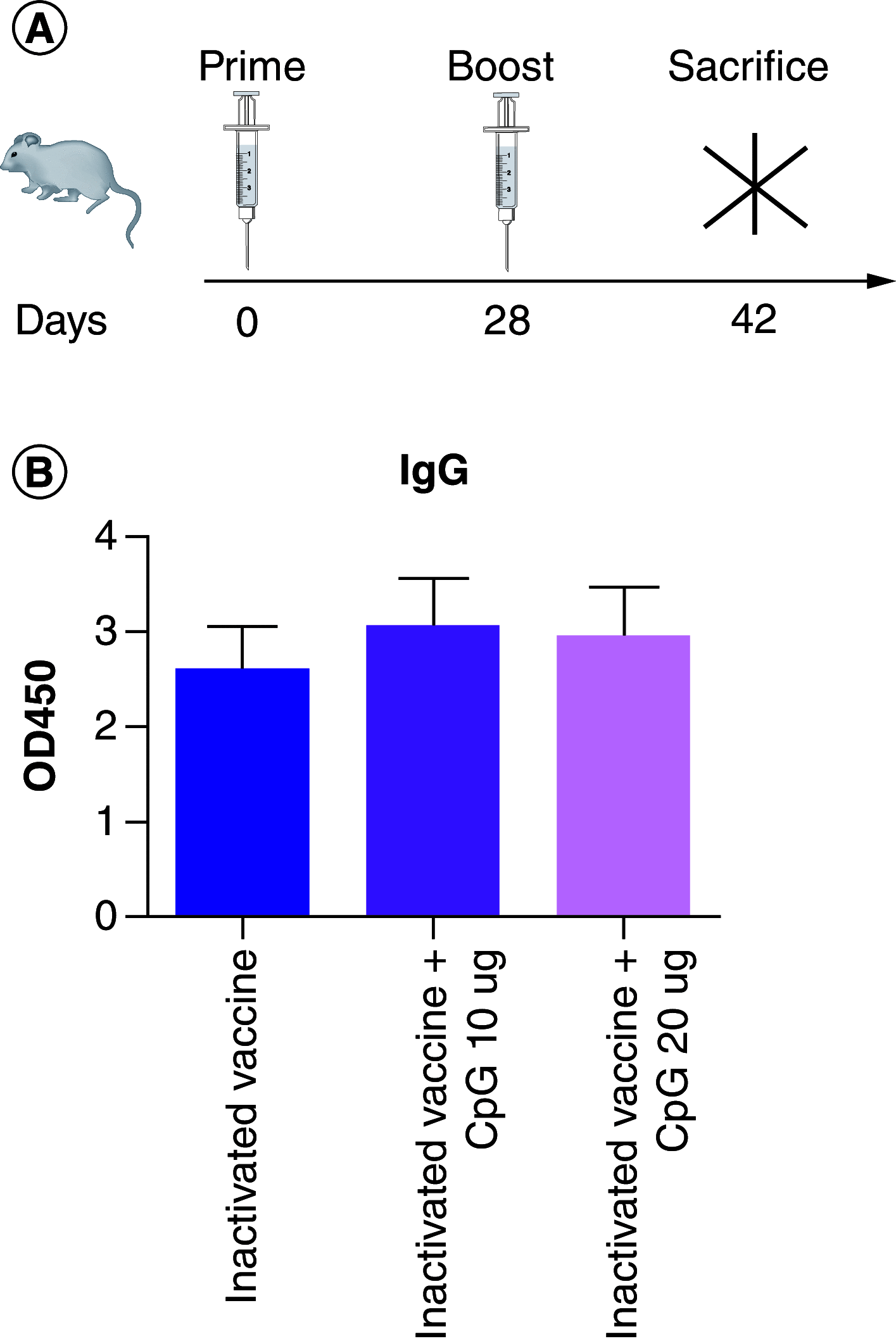
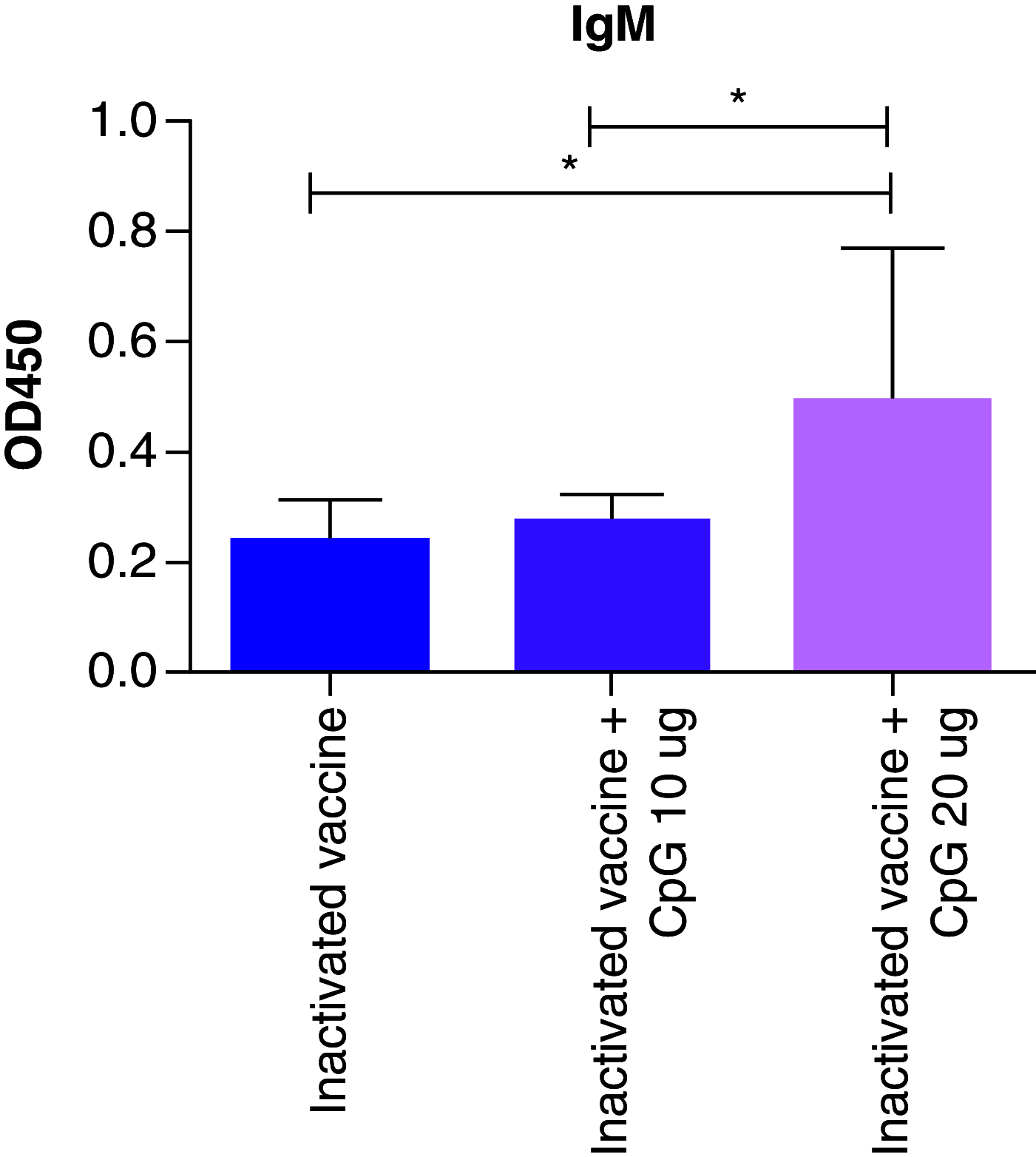
Aim: This study used CpG 684 as adjuvant of inactivated COVID-19 vaccine to detect a humoral and cellular immune response in mice.
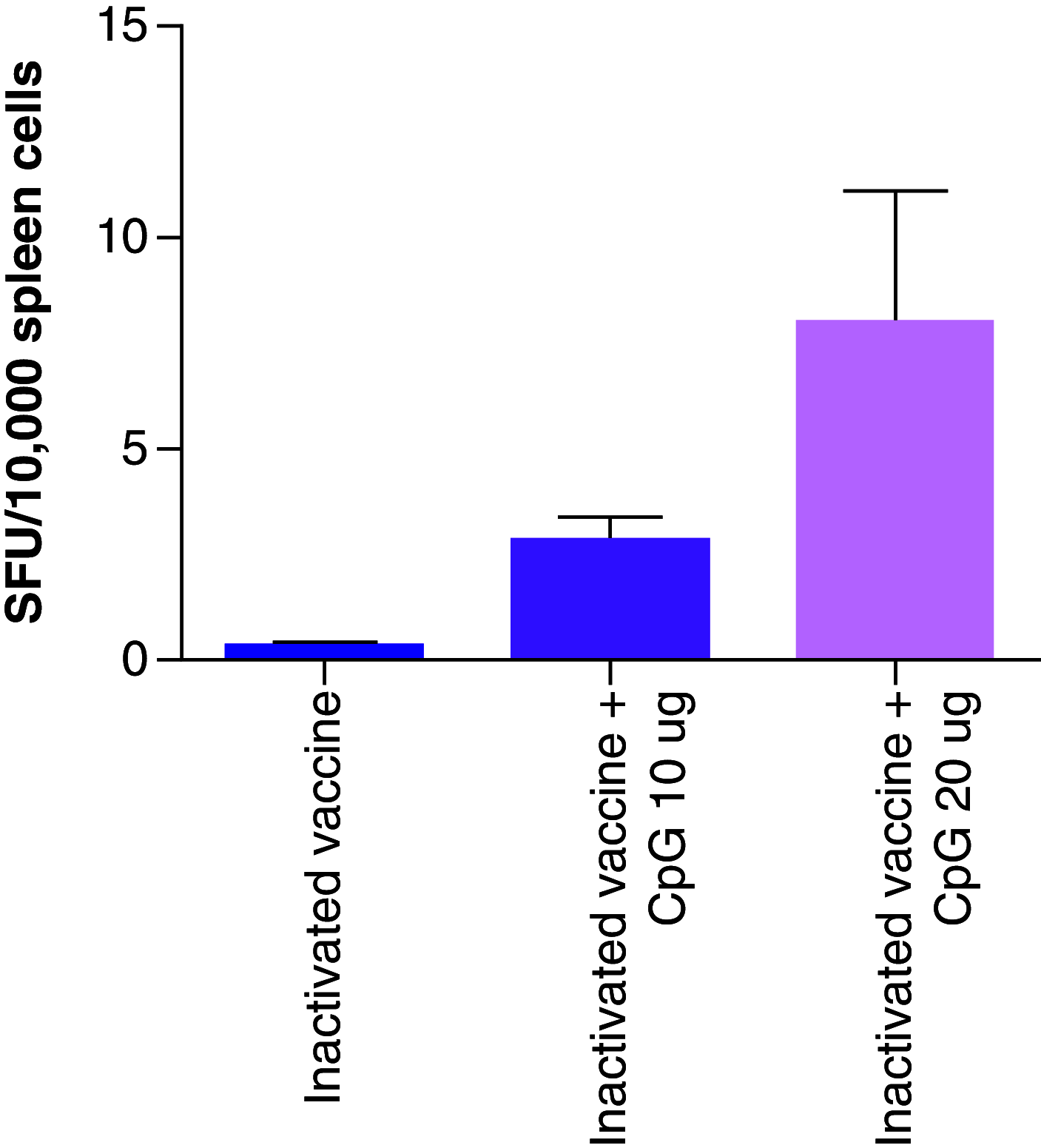
Materials & methods: We used 10 and 20 µg CpG 684 as adjuvants of an inactivated COVID-19 vaccine to immunize mice. IgG, IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b and IgM binding antibodies were detected in serum by ELISA. The IFN-γ cytokine was detected by ELISPOT.
Results: CpG 684 improved spike-specific IgG and IgM subtype binding antibodies and increased the neutralizing antibody titer against prototype, Delta and Beta strains. CpG 684 also improved cellular immune response.
Conclusion: CpG 684 is an effective adjuvant for inactivated COVID-19 vaccine.
Keywords: CpG; SARS-COV-2; neutralizing antibody; vaccine; variants.
© 2023 Future Medicine Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest disclosure The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest present.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Immunogenicity of CpG, MF59-like, and Alum Adjuvant Delta Strain Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines in Mice.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Jan 7;12(1):60. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12010060. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38250873 Free PMC article.
-
Different Formulations of Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Candidates in Human Compatible Adjuvants: Potency Studies in Mice Showed Different Platforms of Immune Responses.Viral Immunol. 2022 Dec;35(10):663-672. doi: 10.1089/vim.2022.0022. Viral Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36534465
-
The immunogenicity of Alum+CpG adjuvant SARS-CoV-2 inactivated vaccine in mice.Vaccine. 2023 Sep 22;41(41):6064-6071. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2023.08.061. Epub 2023 Aug 26. Vaccine. 2023. PMID: 37640568
-
Safety and immunogenicity of S-Trimer (SCB-2019), a protein subunit vaccine candidate for COVID-19 in healthy adults: a phase 1, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.Lancet. 2021 Feb 20;397(10275):682-694. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00241-5. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Lancet. 2021. PMID: 33524311 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Alum/CpG Adjuvanted Inactivated COVID-19 Vaccine with Protective Efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 and Variants.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Jul 29;10(8):1208. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10081208. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36016098 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adiga R, Nayak V. Emergence of novel SARS-CoV-2 variants in India: second wave. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 15, 1578–1583 (2021). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
